Architecture
Deep dive into VoIPBIN’s internal architecture, microservices, communication patterns, and deployment.
Note
AI Context
This section provides comprehensive documentation of VoIPBIN’s system internals. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand how the platform is built, how services communicate, or how infrastructure is deployed. For API usage, see the individual resource documentation pages.
Overview
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s high-level system architecture, including the three major layers (API gateway, microservices, real-time communication) and core design principles. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand the overall platform structure, service categories, or technology stack choices.
VoIPBIN is a cloud-native Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) built on modern microservices architecture. The platform provides comprehensive communication capabilities including PSTN calls, WebRTC, SMS, conferencing, AI-powered features, and workflow orchestration.
VoIPBIN is designed from the ground up for scalability, reliability, and developer productivity, enabling businesses to build sophisticated communication solutions through simple API calls.
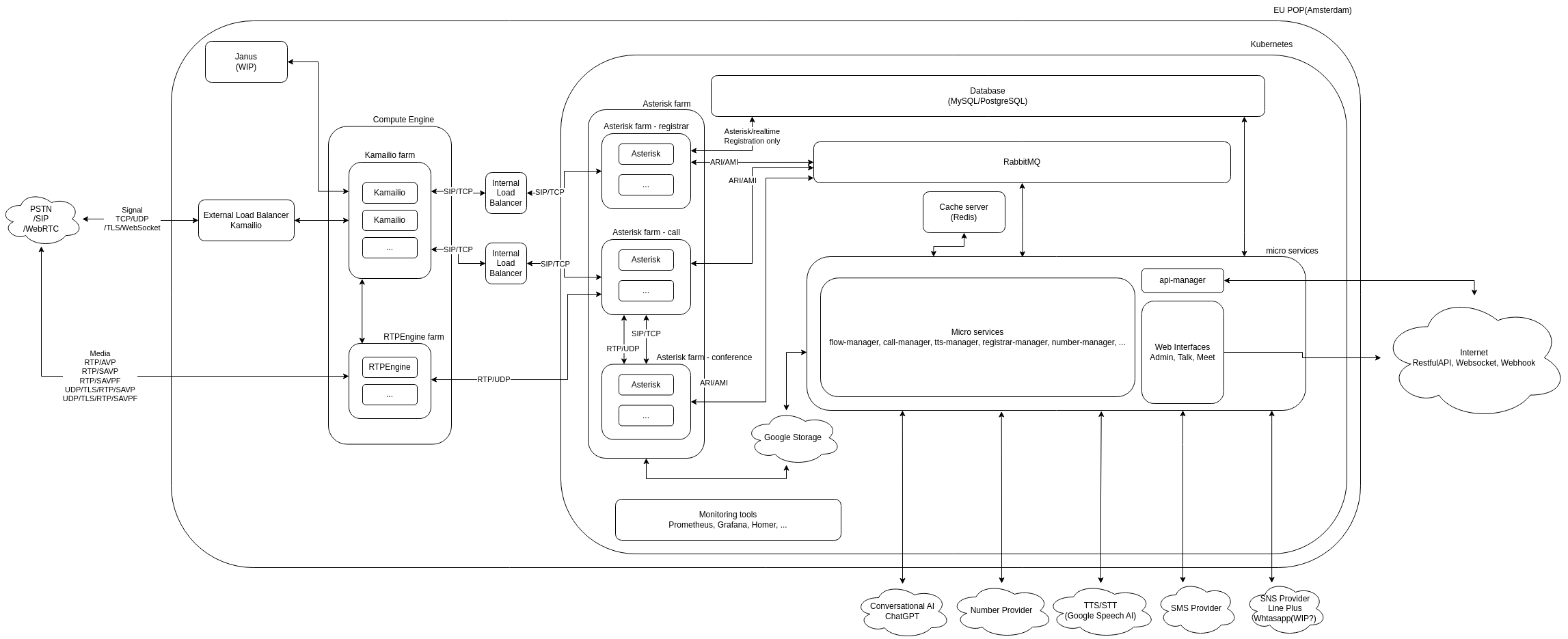
High-Level System Architecture
VoIPBIN consists of three major architectural layers:
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Client Applications |
| (Web Apps, Mobile Apps, Server-to-Server Integrations) |
+------------------------+---------------------------------------------+
| HTTPS/REST API
v
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| API Gateway Layer |
| (bin-api-manager) |
| o Authentication & Authorization |
| o Rate Limiting & Throttling |
| o Request Routing & Load Balancing |
+------------------------+---------------------------------------------+
| RabbitMQ RPC
v
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Microservices Layer |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| | Call Manager | | Flow Manager | | AI Manager | |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| |Chat Manager | | SMS Manager | |Queue Manager | |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| |Agent Manager | | Billing Mgr | |Webhook Mgr | |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| ... 30+ services |
+------------------------+---------------------------------------------+
|
v
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Real-Time Communication Layer |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
| | Kamailio | | Asterisk | | RTPEngine | |
| | (SIP Proxy) | |(Media Server)| |(Media Proxy) | |
| +--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+ |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Shared Infrastructure |
| o MySQL Database o Redis Cache o RabbitMQ o Kubernetes |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------+
Architectural Layers
1. API Gateway Layer
The API Gateway (bin-api-manager) serves as the single entry point for all external requests:
Authentication: JWT-based authentication for all API requests
Authorization: Permission checks based on customer and agent roles
Request Routing: Routes authenticated requests to appropriate backend services via RabbitMQ RPC
Protocol Translation: Converts HTTP/REST to internal RabbitMQ messaging
Response Aggregation: Collects responses from backend services and returns to clients
2. Microservices Layer
VoIPBIN consists of 30+ specialized Go microservices, organized by domain:
Communication Services: * bin-call-manager: Call lifecycle and routing * bin-conference-manager: Conference bridge management * bin-sms-manager: SMS messaging * bin-talk-manager: Real-time chat
AI Services: * bin-ai-manager: AI assistant, transcription, summarization * bin-transcribe-manager: Speech-to-text processing * bin-tts-manager: Text-to-speech synthesis
Workflow Services: * bin-flow-manager: Call flow orchestration and IVR * bin-queue-manager: Call queue management * bin-campaign-manager: Outbound campaign automation
Management Services: * bin-agent-manager: Agent state and presence * bin-billing-manager: Usage tracking and billing * bin-webhook-manager: Webhook delivery * bin-storage-manager: File and media storage
3. Real-Time Communication Layer
See RTC Architecture for detailed information about the VoIP stack.
Core Design Principles
VoIPBIN is designed around these key architectural principles:
Microservices Architecture
Service Isolation:
+------------+ +------------+ +------------+
| Service A | | Service B | | Service C |
| | | | | |
| o Domain | | o Domain | | o Domain |
| o Logic | | o Logic | | o Logic |
| o Data | | o Data | | o Data |
+------+-----+ +------+-----+ +------+-----+
| | |
+------------------+------------------+
Message Queue (RabbitMQ)
Domain Isolation: Each service owns its domain logic and data
Independent Deployment: Services can be deployed independently
Technology Flexibility: Services can use different technologies as needed
Fault Isolation: Failure in one service doesn’t cascade
Event-Driven Architecture
Event Flow:
+--------------+ Event +--------------+
| Service |----------------> | Message |
| (Publisher) | | Queue |
+--------------+ +-------+------+
|
+----------------+
| |
v v
+------------+ +------------+
| Subscriber | | Subscriber |
| Service A | | Service B |
+------------+ +------------+
Asynchronous Communication: Services communicate via events
Loose Coupling: Publishers don’t know about subscribers
Scalability: Multiple subscribers can process events in parallel
Reliability: Message queues provide guaranteed delivery
API Gateway Pattern
External Request Flow:
Client App API Gateway Backend Services
| | |
| HTTPS/REST | |
+---------------------------> |
| | 1. Authenticate |
| | 2. Authorize |
| | 3. Route Request |
| | |
| | RabbitMQ RPC |
| +--------------------------->
| | |
| | Response |
| <---------------------------+
| JSON Response | |
<---------------------------+ |
| | |
Single Entry Point: All external traffic goes through one gateway
Security Layer: Authentication and authorization at the edge
Protocol Translation: HTTP to internal messaging protocols
Service Discovery: Gateway knows how to reach all services
Shared Data Layer
Data Architecture:
+------------+ +------------+ +------------+
| Service | | Service | | Service |
| A | | B | | C |
+------+-----+ +-------+----+ +--------+---+
| | |
+----------------+----------------+
| | |
v v v
+-------------------------------------------+
| Redis Cache (Hot Data) |
+-------------------------------------------+
v v v
+-------------------------------------------+
| MySQL Database (Cold Data) |
+-------------------------------------------+
Shared MySQL: Single source of truth for all data
Redis Cache: Fast access to frequently used data
Consistent Schema: All services use common database schema
Transaction Support: ACID guarantees for critical operations
Communication Channels
VoIPBIN supports multiple communication channels through dedicated gateways:
Voice Communication:
PSTN: Traditional phone calls via carrier integrations
WebRTC: Browser-based voice and video calls
SIP: Direct SIP trunking for enterprise customers
Messaging:
SMS: Text messaging via carrier integrations
Chat: Real-time chat with WebSocket support
Email: Email notifications and campaigns
AI-Enhanced Communication:
AI Assistants: Voice-enabled AI agents for customer service
Transcription: Real-time and batch speech-to-text
Summarization: Call summarization and insights
Sentiment Analysis: Real-time emotion detection
Integration Capabilities
VoIPBIN provides multiple integration methods:
REST API:
Comprehensive REST API for all platform features
OpenAPI/Swagger documentation
SDKs for multiple languages
WebSocket:
Real-time event streaming
Bi-directional media streaming
Live transcription feeds
Webhooks:
Event notifications to external systems
Configurable retry policies
Signature verification for security
Direct Database Access:
Read replicas for reporting
Analytics database for business intelligence
Key Architectural Benefits
VoIPBIN’s architecture is designed to deliver these advantages:
Scalability
Horizontal Scaling: Add more service instances to handle increased load
Independent Scaling: Scale only the services that need more capacity
Auto-Scaling: Kubernetes automatically scales based on metrics
Global Distribution: Deploy services across multiple regions
Reliability
Fault Isolation: Issues in one service don’t affect others
Circuit Breakers: Prevent cascading failures
Automatic Failover: Kubernetes restarts failed containers
SIP Session Recovery: Maintain calls even when servers crash
Message Persistence: RabbitMQ ensures no messages are lost
Security
API Gateway Security: All authentication at the edge
Service Isolation: Services communicate via internal network only
Encryption: TLS for all external communication
Secret Management: Kubernetes secrets for sensitive data
Audit Logging: Complete audit trail of all operations
Developer Productivity
Simple REST API: Easy to integrate with any application
Comprehensive Docs: Detailed documentation with examples
Webhook Events: Real-time notifications of system events
Test Environment: Sandbox for development and testing
SDK Support: Official SDKs for popular languages
Operational Excellence
Centralized Logging: All logs aggregated in one place
Metrics & Monitoring: Prometheus metrics for all services
Distributed Tracing: Track requests across services
Health Checks: Automated health monitoring
Zero-Downtime Deploys: Rolling updates without service interruption
Service Dependencies
VoIPBIN services have well-defined dependencies for coordinated operations:
Core Service Dependencies:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-api-manager |
| (API Gateway) |
| ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Depends on: ALL backend services for RPC routing |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
|
+-----------------------+-----------------------+
| | |
v v v
+-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
|bin-call-mgr | |bin-flow-mgr | |bin-ai-mgr |
+------+------+ +------+------+ +------+------+
| | |
| | |
v v v
+-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
|bin-billing | |bin-call-mgr | |bin-transcribe|
|bin-webhook | |bin-queue-mgr| |bin-tts-mgr |
|bin-number | |bin-ai-mgr | |bin-pipecat |
+-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
Key Dependency Patterns:
Call Processing Chain:
bin-call-manager
+--> bin-flow-manager (IVR and call flows)
+--> bin-billing-manager (usage tracking)
+--> bin-webhook-manager (event notifications)
+--> bin-transcribe-manager (call transcription)
+--> bin-number-manager (phone number lookup)
AI Voice Pipeline:
bin-pipecat-manager
+--> bin-ai-manager (LLM coordination)
+--> bin-call-manager (call control)
+--> bin-transcribe-manager (STT)
Flow Orchestration:
bin-flow-manager
+--> bin-call-manager (call actions)
+--> bin-queue-manager (queue operations)
+--> bin-ai-manager (AI interactions)
+--> bin-conference-manager (conference bridges)
Infrastructure Monitoring:
bin-sentinel-manager
+--> bin-call-manager (SIP session recovery events)
Circular Dependencies:
VoIPBIN avoids circular dependencies through:
Event-Driven Decoupling: Services publish events, others subscribe
Gateway Orchestration: API Gateway coordinates cross-service operations
Shared Data Layer: Services share data via MySQL, not direct calls
Technology Stack
VoIPBIN is built on modern, proven technologies:
Backend Services:
Language: Go (Golang) for all microservices
API Framework: Gin for HTTP routing
RPC: RabbitMQ for inter-service communication
Database: MySQL for persistent storage
Cache: Redis for session and hot data
Real-Time Communication:
SIP Proxy: Kamailio for SIP routing
Media Server: Asterisk for call processing
Media Proxy: RTPEngine for RTP handling
Infrastructure:
Container Runtime: Docker for containerization
Orchestration: Kubernetes (GKE) for container management
Cloud Provider: Google Cloud Platform
Monitoring: Prometheus + Grafana for metrics
Logging: ELK stack for centralized logging
Message Queue:
Broker: RabbitMQ for async messaging
Event Bus: ZeroMQ for pub/sub events
This architecture enables VoIPBIN to deliver enterprise-grade communication services at scale while maintaining developer simplicity and operational excellence.
Backend Microservices
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s 30+ Go microservices, their organization by domain, the API gateway (bin-api-manager), and special service architectures (pipecat hybrid Go/Python, sentinel Kubernetes monitoring). Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand which service handles a specific domain, the routing table from HTTP endpoints to backend services, or the authentication/authorization flow.
VoIPBIN’s backend consists of 30+ specialized Go microservices organized into functional domains. Each service owns its specific business logic and communicates with others through a message queue, enabling independent scaling, deployment, and development.
Microservices Organization
Services are organized by functional domain:
VoIPBIN Microservices Architecture
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Communication Services |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-call-manager | Call lifecycle and routing |
| bin-conference-manager | Conference bridge management |
| bin-message-manager | SMS messaging (Telnyx/MsgBird) |
| bin-talk-manager | Real-time chat |
| bin-email-manager | Email campaigns |
| bin-transfer-manager | Call transfer operations |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| AI Services |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-ai-manager | AI assistants and processing |
| bin-transcribe-manager | Speech-to-text transcription |
| bin-tts-manager | Text-to-speech synthesis |
| bin-pipecat-manager | Real-time AI voice (Go/Python) |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Workflow Services |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-flow-manager | Call flow and IVR orchestration |
| bin-queue-manager | Call queue management |
| bin-campaign-manager | Outbound campaign automation |
| bin-outdial-manager | Outbound dialing targets |
| bin-conversation-manager| Conversation tracking |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Management Services |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-agent-manager | Agent state and presence |
| bin-billing-manager | Usage tracking and billing |
| bin-customer-manager | Customer and API key management |
| bin-webhook-manager | Webhook delivery |
| bin-storage-manager | File, media, and recordings |
| bin-number-manager | Phone number management |
| bin-tag-manager | Customer tag management |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Integration Services |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-talk-manager | Agent UI backend |
| bin-hook-manager | External webhook gateway |
| bin-sentinel-manager | Kubernetes pod monitoring |
| bin-route-manager | Call routing and providers |
| bin-registrar-manager | SIP registration management |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
Service Characteristics
Each microservice follows these design principles:
Domain Isolation
Service Boundary:
+----------------------------------------+
| bin-call-manager |
| |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Domain Logic (Call Handling) | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Data Access (Call Records) | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | RPC Handlers (Message Queue) | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
+----------------------------------------+
Single Responsibility: Each service owns one specific domain
Encapsulated Logic: Business rules contained within the service
Data Ownership: Service owns its database tables and schema
Clear Boundaries: Well-defined interfaces and APIs
Technology Stack
All backend services share a common technology stack:
Language: Go (Golang) 1.21+
HTTP Framework: Gin for REST endpoints (when needed)
Database: MySQL 8.0 via sqlx
Cache: Redis 7.0 via go-redis
Message Queue: RabbitMQ via bin-common-handler
Logging: Structured logging with logrus
Monitoring: Prometheus metrics
Common Structure
All services follow a consistent directory structure:
bin-<service>-manager/
+-- cmd/
| +-- <service>-manager/
| +-- main.go # Entry point
+-- pkg/
| +-- <domain>handler/ # Business logic
| +-- dbhandler/ # Database operations
| +-- cachehandler/ # Redis operations
| +-- listenhandler/ # RabbitMQ RPC handlers
+-- models/
| +-- <resource>/ # Data models
+-- go.mod # Dependencies
API Gateway - bin-api-manager
The API Gateway serves as the single entry point for all external requests, handling authentication, authorization, and request routing to backend services.
Gateway Responsibilities
API Gateway Layer:
External Clients
(Web, Mobile, Server)
|
| HTTPS
v
+----------------------------------------+
| bin-api-manager |
| |
| 1. +----------------------------+ |
| | Authentication (JWT) | |
| +----------------------------+ |
| |
| 2. +-----------------------------+ |
| | Authorization (Permissions)| |
| +-----------------------------+ |
| |
| 3. +----------------------------+ |
| | Rate Limiting / Throttling| |
| +----------------------------+ |
| |
| 4. +----------------------------+ |
| | Request Routing (RabbitMQ)| |
| +----------------------------+ |
| |
| 5. +----------------------------+ |
| | Response Aggregation | |
| +----------------------------+ |
+----------------------------------------+
|
| RabbitMQ RPC
v
Backend Services
Authentication Flow
JWT Authentication:
Client API Gateway Backend Service
| | |
| POST /auth/login | |
+--------------------------->> |
| {user, pass} | |
| | |
| | Verify credentials |
| | |
| JWT Token | |
<<---------------------------+ |
| | |
| | |
| GET /calls?token=xyz | |
+--------------------------->> |
| | 1. Validate JWT |
| | 2. Extract customer_id |
| | 3. Check permissions |
| | |
| | RPC: GetCalls(ctx) |
| +------------------------->>
| | |
| | [Call List] |
| <<-------------------------+
| | |
| [Call List] | 4. Return response |
<<---------------------------+ |
| | |
Authentication Components:
JWT Validation: Validates token signature and expiration
Customer Extraction: Extracts customer_id from JWT claims
Permission Check: Verifies user has required permissions
Context Propagation: Passes auth context to backend services
Authorization Pattern
VoIPBIN implements authorization at the API Gateway, NOT in backend services:
Authorization Check:
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| bin-api-manager (Gateway) |
| |
| 1. Fetch Resource |
| +-------> bin-call-manager.GetCall(call_id) |
| | |
| 2. Check Authorization |
| | if call.customer_id != jwt.customer_id: |
| | return 404 (not 403, for security) |
| | |
| 3. Return Resource |
| +-------> return call |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| bin-call-manager (Backend) |
| |
| o NO authentication logic |
| o NO customer_id validation |
| o Just process RPC requests |
| o Return requested data |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
Key Authorization Principles:
Gateway-Only Auth: All authorization logic in bin-api-manager
Fetch-Then-Check: Fetch resource first, then verify ownership
Return 404, Not 403: Return “not found” for unauthorized access (security)
Backend Trust: Backend services trust the gateway
Request Routing
The gateway routes requests to appropriate backend services:
Routing Decision:
HTTP Request Gateway Router Backend Service
| | |
| GET /v1.0/calls | |
+--------------------->> |
| | Parse: "calls" |
| | -> bin-call-manager |
| | |
| | RPC Request |
| +----------------------->>
| | |
| | RPC Response |
| <<-----------------------+
| | |
| JSON Response | |
<<---------------------+ |
| | |
Routing Table:
HTTP Endpoint |
Backend Service |
|---|---|
/v1.0/calls |
bin-call-manager |
/v1.0/conferences |
bin-conference-manager |
/v1.0/messages |
bin-message-manager |
/v1.0/talks |
bin-talk-manager |
/v1.0/emails |
bin-email-manager |
/v1.0/agents |
bin-agent-manager |
/v1.0/queues |
bin-queue-manager |
/v1.0/campaigns |
bin-campaign-manager |
/v1.0/outdials |
bin-outdial-manager |
/v1.0/flows |
bin-flow-manager |
/v1.0/conversations |
bin-conversation-manager |
/v1.0/billings |
bin-billing-manager |
/v1.0/customers |
bin-customer-manager |
/v1.0/webhooks |
bin-webhook-manager |
/v1.0/transcribes |
bin-transcribe-manager |
/v1.0/numbers |
bin-number-manager |
/v1.0/routes |
bin-route-manager |
/v1.0/tags |
bin-tag-manager |
/v1.0/storage |
bin-storage-manager |
/v1.0/transfers |
bin-transfer-manager |
Special Service Architectures
Some services have unique architectures that differ from the standard microservice pattern:
bin-pipecat-manager (Hybrid Go/Python)
This service combines Go and Python for AI-powered voice conversations:
Hybrid Architecture:
+------------------------------------------------------------+
| bin-pipecat-manager |
| |
| Go Service (Port 8080) Python Service (Port 8000)|
| +---------------------+ +---------------------+ |
| | o RabbitMQ RPC | HTTP | o FastAPI server | |
| | o WebSocket server |<------>| o Pipecat pipelines | |
| | o Session lifecycle | | o STT/LLM/TTS | |
| | o Audiosocket (RTP) | | o Tool execution | |
| +----------+----------+ +---------------------+ |
| | |
+--------------|---------------------------------------------+
|
| Audiosocket (8kHz PCM)
v
Asterisk PBX
Audio Flow:
Asterisk (8kHz) --audiosocket--> Go --websocket/protobuf--> Python
<-----------------------
STT -> LLM -> TTS pipeline executed in Python/Pipecat
Key Features:
Dual Runtime: Go for infrastructure, Python for AI pipelines
Protobuf Frames: Efficient audio frame serialization
Sample Rate Conversion: 8kHz (Asterisk) ↔ 16kHz (AI services)
Tool Calling: LLM can invoke VoIP functions (connect_call, send_email)
bin-sentinel-manager (Kubernetes Monitoring)
This service monitors pod lifecycle events in Kubernetes:
Kubernetes Monitoring:
+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| Kubernetes Cluster (voip namespace) |
| |
| +------------+ +------------+ +------------+ |
| | asterisk- | | asterisk- | | asterisk- | |
| | call | | conference | | registrar | |
| +------+-----+ +------+-----+ +------+-----+ |
| | | | |
| +---------------+---------------+ |
| | |
| Pod Events (Update/Delete) |
| | |
| v |
| +-------------------------------+ |
| | bin-sentinel-manager | |
| | | |
| | o Pod informers (client-go) | |
| | o Label selector filtering | |
| | o Event publishing | |
| +---------------+---------------+ |
| | |
+-------------------------|---------------------------------+
|
| RabbitMQ Events
v
+-------------------+
| bin-call-manager |
| (SIP Recovery) |
+-------------------+
Key Features:
In-Cluster Monitoring: Uses Kubernetes client-go with RBAC
Label-Based Filtering: Watches specific pod labels (app=asterisk-*)
Event Publishing: Notifies services via RabbitMQ for recovery actions
Prometheus Metrics: Exports pod state change counters
SIP Session Recovery: Enables call-manager to recover sessions when pods crash
bin-hook-manager (Webhook Gateway)
This service receives external webhooks and routes them internally:
External Webhook Flow:
External Provider VoIPBIN Internal
(Telnyx, MessageBird) Services
| |
| HTTPS POST |
| /v1.0/hooks/messages |
v |
+-----------------+ |
| bin-hook-manager| |
| | RabbitMQ |
| o Validate +------------------------>| bin-message-manager
| o Parse | | bin-email-manager
| o Route | | bin-conversation-manager
+-----------------+ |
Key Features:
Public Endpoint: Receives webhooks from external providers
Message Routing: Forwards to internal services via RabbitMQ
Provider Support: Handles Telnyx, MessageBird delivery notifications
Thin Proxy: No business logic, just routing
Service Independence
VoIPBIN’s microservices architecture enables true service independence:
Independent Deployment
Service Deployment:
+--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+
| Service A | | Service B | | Service C |
| v1.2.3 | | v2.0.1 | | v1.5.0 |
+------+-------+ +------+-------+ +------+-------+
| | |
| | Deploy v2.1.0 |
| | (no impact) |
| v |
| +--------------+ |
| | Service B | |
| | v2.1.0 | |
| +--------------+ |
| | |
+-----------------+-----------------+
Message Queue
No Downtime: Services update without affecting others
Version Independence: Each service has its own version
Gradual Rollout: Can deploy to subset of instances
Quick Rollback: Easy to revert problematic deployments
Independent Scaling
Horizontal Scaling:
Normal Load: High Call Load:
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| Call | | Call | | Call | | Call |
| Manager | | Manager | | Manager | | Manager |
| x1 | | x1 | | x2 | | x3 |
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +----------+
+----------+ +----------+
| SMS | | SMS |
| Manager | | Manager |
| x1 | | x1 |
+----------+ +----------+
Scale only what needs scaling
Targeted Scaling: Scale only services experiencing load
Cost Optimization: Don’t over-provision underutilized services
Auto-Scaling: Kubernetes HPA scales based on metrics
Resource Efficiency: Better resource utilization
Independent Development
Development Isolation:
Team A Team B Team C
| | |
| bin-call- | bin-flow- | bin-ai-
| manager | manager | manager
| | |
| o Go codebase | o Go codebase | o Go codebase
| o Own git | o Own git | o Own git
| branch | branch | branch
| o Own CI/CD | o Own CI/CD | o Own CI/CD
| o Own tests | o Own tests | o Own tests
| | |
+-------------------+-------------------+
Coordinate only via:
o Message contracts
o Database schema
o API contracts
Team Autonomy: Teams work independently
Faster Development: No coordination bottleneck
Technology Flexibility: Can use different libraries
Clear Ownership: Each team owns specific domains
Service Communication Patterns
Services communicate primarily through RabbitMQ RPC:
Synchronous RPC (Request-Response)
RPC Communication:
API Gateway RabbitMQ Call Manager
| | |
| 1. Call Request | |
+------------------------>> |
| Queue: bin-manager. | |
| call.request | |
| | 2. Dequeue Request |
| +--------------------->>
| | |
| | 3. Process Request |
| | (create call) |
| | |
| | 4. Send Response |
| <<---------------------+
| 5. Response | |
<<------------------------+ |
| | |
Asynchronous Events (Pub/Sub)
Event Broadcasting:
Call Manager RabbitMQ Exchange Subscribers
| | |
| 1. Call Created | |
| (publish event) | |
+--------------------->> |
| | |
| | 2. Broadcast |
| | to all |
| +----------+------------+
| | | |
| | v v
| | +----------+ +----------+
| | | Billing | | Webhook |
| | | Manager | | Manager |
| | +----------+ +----------+
| | |
| | Process event |
| | independently |
Communication Patterns Used:
RPC (Synchronous): For request-response operations (GET, POST, DELETE)
Pub/Sub (Asynchronous): For event notifications (call.created, sms.sent)
Webhooks: For external system notifications
WebSocket: For real-time client updates
Service Discovery and Configuration
VoIPBIN uses a hybrid approach for service discovery:
Queue-Based Discovery
Service Registration:
+------------------------------------------------+
| RabbitMQ Queue Naming |
| |
| bin-manager.<service>.<operation> |
| |
| Examples: |
| o bin-manager.call.request |
| o bin-manager.conference.request |
| o bin-manager.sms.request |
| |
| Services listen on their named queues |
| Clients send to known queue names |
+------------------------------------------------+
Convention-Based: Queue names follow predictable pattern
No Registry: No central service registry needed
Self-Registering: Services create queues on startup
Load Balanced: Multiple instances share same queue
Configuration Management
Services receive configuration through multiple sources:
Configuration Sources:
+----------------+
| Service |
+----+-----------+
|
+-------> Environment Variables
| o Database connection
| o RabbitMQ address
| o Redis address
|
+-------> Command-Line Flags
| o Port number
| o Log level
|
+-------> bin-config-manager
| o Feature flags
| o Business logic config
|
+-------> Database
o Dynamic configuration
o Customer-specific settings
Health Monitoring
All services expose health check endpoints:
Health Check Architecture:
Kubernetes Service Health Dependencies
| | |
| 1. Health Check | |
+---------------------->> |
| GET /health | |
| | 2. Check MySQL |
| +---------------------->>
| | (ping) |
| | |
| | 3. Check Redis |
| +---------------------->>
| | (ping) |
| | |
| | 4. Check RabbitMQ |
| +---------------------->>
| | (connection) |
| | |
| 200 OK / 503 Error | |
<<----------------------+ |
| | |
| 5. Restart if failed | |
| (after retries) | |
Health Check Components:
Liveness Probe: Is the service running?
Readiness Probe: Is the service ready to accept traffic?
Dependency Checks: Are database, cache, queue healthy?
Auto-Recovery: Kubernetes restarts unhealthy pods
Error Handling and Resilience
Services implement multiple resilience patterns:
Circuit Breaker
Circuit Breaker States:
Closed (Normal) Open (Failed) Half-Open (Testing)
| | |
| Requests pass | Requests rejected | Limited requests
| through | immediately | allowed
| | |
| ------------> | --------X | ------------>
| | |
| If failures | After timeout | If success
| exceed threshold | period | threshold met
| | |
+---------------------->> |
<<----------------------+
| |
+---------------------->>
If still failing |
|
+------> Closed
Prevent Cascade Failures: Stop calling failed services
Fast Fail: Return error immediately when circuit open
Auto-Recovery: Periodically test if service recovered
Retry with Backoff
Exponential Backoff:
Attempt 1: Immediate
|
| Failed
v
Attempt 2: Wait 1s
|
| Failed
v
Attempt 3: Wait 2s
|
| Failed
v
Attempt 4: Wait 4s
|
| Failed
v
Attempt 5: Wait 8s
|
| Failed
v
Give up, return error
Transient Failures: Retry on temporary failures
Backoff Strategy: Increase wait time between retries
Max Attempts: Limit total number of retries
Idempotency: Ensure operations safe to retry
Timeouts
All RPC calls have strict timeouts:
Default Timeout: 30 seconds for most operations
Long Operations: 120 seconds for complex workflows
Streaming: No timeout for streaming operations
Context Propagation: Timeout passed through call chain
Deployment Architecture
Services deploy to Kubernetes on Google Cloud Platform:
Kubernetes Deployment:
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| GKE Cluster |
| |
| +---------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Namespace: production | |
| | | |
| | +---------------------------------------------+ | |
| | | Deployment: bin-call-manager | | |
| | | +---------+ +---------+ +---------+ | | |
| | | | Pod 1 | | Pod 2 | | Pod 3 | | | |
| | | +---------+ +---------+ +---------+ | | |
| | | Replicas: 3 HPA: 3-10 | | |
| | +---------------------------------------------+ | |
| | | |
| | +---------------------------------------------+ | |
| | | Deployment: bin-api-manager | | |
| | | +---------+ +---------+ +---------+ | | |
| | | | Pod 1 | | Pod 2 | | Pod 3 | | | |
| | | +---------+ +---------+ +---------+ | | |
| | | Replicas: 3 HPA: 3-20 | | |
| | +---------------------------------------------+ | |
| | | |
| | ... 30+ more deployments | |
| | | |
| +---------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| +---------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Shared Resources (same cluster) | |
| | o MySQL StatefulSet | |
| | o Redis StatefulSet | |
| | o RabbitMQ StatefulSet | |
| | o Prometheus Monitoring | |
| +---------------------------------------------------+ |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
Deployment Characteristics:
Container-Based: Each service runs in Docker containers
Replica Sets: Multiple instances for high availability
Auto-Scaling: HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaler) based on CPU/memory
Rolling Updates: Zero-downtime deployments
Resource Limits: CPU and memory limits per container
Health Probes: Automatic restart of failed containers
Monitoring and Observability
Comprehensive monitoring across all services:
Metrics Collection
Metrics Pipeline:
Services Prometheus Grafana
(30+ services) | |
| | |
| Expose /metrics | |
| endpoint | |
| | |
| Scrape every 15s | |
+--------------------->> |
| | |
| | Time-series DB |
| | stores metrics |
| | |
| | Query metrics |
| +--------------------->>
| | |
| | Visualize |
| | dashboards |
| | |
Key Metrics:
Request Rate: Requests per second per service
Error Rate: Failed requests percentage
Latency: P50, P95, P99 response times
Resource Usage: CPU, memory, disk per pod
Queue Depth: RabbitMQ queue backlogs
Database Connections: Active connections per service
Logging
All services use structured logging:
{
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"level": "info",
"service": "bin-call-manager",
"instance": "pod-xyz",
"message": "Call created successfully",
"call_id": "abc-123-def",
"customer_id": "customer-789",
"duration_ms": 45
}
Structured Format: JSON logs for easy parsing
Centralized Collection: All logs aggregated in one place
Searchable: Full-text search across all services
Correlation IDs: Track requests across services
Best Practices
VoIPBIN’s backend follows these best practices:
Service Design:
One service, one responsibility
Services communicate via messages, not direct calls
Shared database, but logical isolation by tables
Idempotent operations for safe retries
Error Handling:
Always return errors, never panic
Use context for timeouts and cancellation
Implement circuit breakers for external dependencies
Log errors with full context
Performance:
Use connection pooling for database and Redis
Implement caching for frequently accessed data
Use batch operations where possible
Monitor and optimize hot paths
Security:
No authentication logic in backend services
Trust the API gateway for auth decisions
Validate all inputs at service boundaries
Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection
Testing:
Unit tests for business logic
Integration tests with mock dependencies
End-to-end tests for critical flows
Load tests before production deployment
Inter-Service Communication
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s inter-service communication patterns: RabbitMQ RPC (synchronous request-response), RabbitMQ pub/sub (asynchronous events), ZeroMQ (high-performance real-time streaming), and WebSocket (client notifications). Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand how services talk to each other, message reliability guarantees, queue naming conventions, or event types.
VoIPBIN’s microservices communicate through multiple messaging patterns optimized for different use cases. The architecture uses RabbitMQ for RPC and pub/sub, ZeroMQ for high-performance events, and WebSocket for real-time client communication.
Communication Patterns Overview
VoIPBIN uses three primary communication mechanisms:
Communication Architecture:
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| RabbitMQ (Primary Bus) |
| |
| +-----------------------+ +-----------------------+ |
| | RPC (Synchronous) | | Pub/Sub (Async) | |
| | Request-Response | | Event Broadcasting | |
| +-----------------------+ +-----------------------+ |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| ZeroMQ (High-Performance Events) |
| |
| o Real-time event streaming |
| o Agent presence updates |
| o Call state changes |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| WebSocket (Client Communication) |
| |
| o Real-time client notifications |
| o Bi-directional media streaming |
| o Live transcription feeds |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
RabbitMQ RPC Pattern
VoIPBIN uses RabbitMQ for synchronous request-response communication between services.
RPC Flow
RPC Request-Response Pattern:
Client Service RabbitMQ Server Service
| | |
| 1. Send Request | |
| +------------+ | |
| | call_id | | |
| | action | | |
| | reply_to | | |
| +------------+ | |
+-------------------->> |
| Queue: bin-manager.| |
| call.request| |
| | 2. Dequeue |
| +---------------------->>
| | |
| | 3. Process Request |
| | (business logic) |
| | |
| | 4. Send Response |
| <<----------------------+
| | Queue: reply_to |
| 5. Receive Response| |
<<--------------------+ |
| +------------+ | |
| | status | | |
| | data | | |
| | error | | |
| +------------+ | |
| | |
Queue Naming Convention
All RPC queues follow a consistent naming pattern:
Queue Name Format:
bin-manager.<service>.<operation>
Examples:
o bin-manager.call.request -> bin-call-manager
o bin-manager.conference.request -> bin-conference-manager
o bin-manager.sms.request -> bin-sms-manager
o bin-manager.flow.request -> bin-flow-manager
o bin-manager.billing.request -> bin-billing-manager
Message Structure
RPC messages use a standardized JSON format:
Request Message:
{
"message_id": "uuid-v4",
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"route": "/v1/calls",
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"customer_id": "customer-123",
"agent_id": "agent-456"
},
"body": {
"source": {"type": "tel", "target": "+15551234567"},
"destinations": [{"type": "tel", "target": "+15559876543"}]
}
}
Response Message:
{
"message_id": "uuid-v4",
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:01.000Z",
"status_code": 200,
"body": {
"id": "call-789",
"status": "ringing",
...
},
"error": null
}
RPC Implementation Pattern
Services implement RPC handlers following this pattern:
Service RPC Handler:
+------------------------------------------------+
| bin-call-manager |
| |
| 1. Listen on Queue |
| +- bin-manager.call.request |
| | |
| 2. Receive Message |
| +- Deserialize JSON |
| +- Validate request |
| | |
| 3. Route to Handler |
| +- Parse route: POST /v1/calls |
| +- Call: CallCreate(ctx, req) |
| | |
| 4. Execute Business Logic |
| +- Validate data |
| +- Create call record |
| +- Initiate SIP call |
| | |
| 5. Send Response |
| +- Serialize result |
| +- Reply to reply_to queue |
| |
+------------------------------------------------+
Load Balancing
Multiple service instances share the same queue:
Load Balanced RPC:
API Gateway Queue Service Instances
| | |
| Request 1 | |
+--------------------->> |
| +---------------------->> Instance 1
| | (round-robin) | (processes req 1)
| | |
| Request 2 | |
+--------------------->> |
| +---------------------->> Instance 2
| | (round-robin) | (processes req 2)
| | |
| Request 3 | |
+--------------------->> |
| +---------------------->> Instance 3
| | (round-robin) | (processes req 3)
| | |
Fair Distribution: RabbitMQ distributes messages evenly
No Coordination: Instances don’t need to know about each other
Dynamic Scaling: Add/remove instances without configuration
Automatic Recovery: If instance fails, messages redelivered
RabbitMQ Pub/Sub Pattern
For asynchronous event notifications, VoIPBIN uses RabbitMQ’s pub/sub (fanout exchange) pattern.
Pub/Sub Flow
Event Publishing Pattern:
Publisher Exchange Subscribers
| | |
| 1. Publish Event | |
| +------------+ | |
| |event: call | | |
| | .created| | |
| |data: {...} | | |
| +------------+ | |
+--------------------->> |
| Exchange: | |
| call.events | |
| | 2. Fanout to all |
| | subscribers |
| +------+----------------+
| | | |
| | v v
| | +--------+ +--------+
| | |Billing | |Webhook |
| | |Manager | |Manager |
| | +--------+ +--------+
| | | |
| | 3. Process 3. Process
| | event event
| | independently independently
Event Types
VoIPBIN publishes events for major state changes:
Event Categories:
Call Events:
o call.created - New call initiated
o call.ringing - Call ringing
o call.answered - Call answered
o call.ended - Call terminated
Conference Events:
o conference.created - Conference created
o conference.participant_joined
o conference.participant_left
o conference.ended
SMS Events:
o sms.sent - SMS sent successfully
o sms.delivered - SMS delivered to recipient
o sms.failed - SMS delivery failed
Agent Events:
o agent.login - Agent logged in
o agent.logout - Agent logged out
o agent.status_change - Agent status changed
Transcription Events:
o transcribe.started - Transcription started
o transcribe.completed
o transcript.created - New transcript segment
Event Message Structure
Event Message Format:
{
"event_id": "uuid-v4",
"event_type": "call.created",
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"customer_id": "customer-123",
"resource_type": "call",
"resource_id": "call-789",
"data": {
"id": "call-789",
"source": "+15551234567",
"destination": "+15559876543",
"status": "ringing",
...
}
}
Subscriber Pattern
Services subscribe to events they’re interested in:
Subscriber Implementation:
+------------------------------------------------+
| bin-billing-manager |
| |
| 1. Declare Exchange |
| +- call.events (fanout) |
| |
| 2. Create Queue |
| +- billing.call.events (unique) |
| |
| 3. Bind Queue to Exchange |
| +- Receive all events from exchange |
| |
| 4. Consume Events |
| +- call.created -> Track call start |
| +- call.answered -> Start billing |
| +- call.ended -> Calculate charges |
| +- Other events -> Ignore |
| |
+------------------------------------------------+
Event Processing Guarantees
Event Processing:
+--------------+
| Publish |
+------+-------+
|
| RabbitMQ persists event
| (survives broker restart)
v
+--------------+
| Deliver |
+------+-------+
|
| Subscriber processes
| (may retry on failure)
v
+--------------+
| ACK |
+--------------+
|
| Remove from queue
| (event processed successfully)
v
+--------------+
| Complete |
+--------------+
At-Least-Once Delivery: Events delivered at least once (may duplicate)
Persistent: Events survive broker restart
Manual ACK: Subscriber acknowledges after processing
Retry on Failure: Redelivered if subscriber crashes
ZeroMQ Event Streaming
For high-performance, low-latency event streaming, VoIPBIN uses ZeroMQ pub/sub sockets.
ZMQ Architecture
ZeroMQ Pub/Sub Pattern:
Publishers Subscribers
| |
| Call Manager |
| (publishes call events) |
+----------------------+ |
| ZMQ PUB Socket | |
| tcp://*:5555 | |
+----------+-----------+ |
| |
| Event Stream |
| (no broker) |
| |
+---------------------------->> Agent Manager
| | (agent presence)
| |
+---------------------------->> Webhook Manager
| | (webhook delivery)
| |
+---------------------------->> Talk Manager
| (agent UI updates)
Key Differences from RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ vs ZeroMQ:
RabbitMQ: ZeroMQ:
+------------+ +------------+
| Publisher | | Publisher |
+------+-----+ +------+-----+
| |
| Reliable | Fast
| Persistent | In-memory
| Broker-based | Direct socket
v v
+------------+ +------------+
| RabbitMQ | | Subscriber |
| Broker | | (Direct) |
+------+-----+ +------------+
|
| At-least-once
v
+------------+
| Subscriber |
+------------+
RabbitMQ: * Persistent, reliable * Guaranteed delivery * Message queuing * Higher latency (~10ms)
ZeroMQ: * In-memory, fast * Best-effort delivery * Direct sockets * Lower latency (<1ms)
Use Cases
VoIPBIN uses ZeroMQ for:
ZeroMQ Use Cases:
[x] Agent Presence Updates
o Agent login/logout
o Status changes (available, busy, away)
o Real-time UI updates
o High frequency, acceptable loss
[x] Call State Changes
o Call ringing, answered, ended
o Conference participant updates
o Duplicate with RabbitMQ (redundant)
o Speed over reliability
[x] Real-Time Metrics
o Queue statistics
o Active call counts
o System health metrics
o Dashboard updates
[ ] NOT Used For:
o Billing events (use RabbitMQ)
o Webhook delivery (use RabbitMQ)
o Critical state changes (use RabbitMQ)
ZMQ Message Format
ZMQ Message Structure:
Topic (routing key)
|
+- "agent.presence"
| {
| "agent_id": "agent-123",
| "status": "available",
| "timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z"
| }
|
+- "call.state"
| {
| "call_id": "call-789",
| "status": "answered",
| "timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:01.000Z"
| }
|
+- "queue.stats"
{
"queue_id": "queue-456",
"waiting": 5,
"active": 3
}
Topic Filtering
Subscribers can filter events by topic:
Topic-Based Filtering:
Subscriber A:
o Subscribe to: "agent.*"
o Receives:
- agent.presence
- agent.login
- agent.logout
Subscriber B:
o Subscribe to: "call.*"
o Receives:
- call.state
- call.metrics
Subscriber C:
o Subscribe to: "" (empty = all)
o Receives: everything
WebSocket Communication
For real-time client communication, VoIPBIN uses WebSocket connections.
WebSocket Architecture
WebSocket Connection Flow:
Client (Browser/App) API Gateway Backend Services
| | |
| 1. HTTP Upgrade | |
| (WebSocket) | |
+--------------------->> |
| | 2. Authenticate |
| | (JWT token) |
| | |
| 3. Connection | |
| Established | |
<<---------------------+ |
| | |
| 4. Subscribe | |
| {"type":"subscribe",| |
| "topics":["..."]} | |
+--------------------->> |
| | 5. Register |
| | subscription |
| | |
| | 6. Backend Event |
| <<----------------------+
| | (via RabbitMQ/ZMQ) |
| | |
| 7. Push to Client | |
<<---------------------+ |
| {"event":"call. | |
| created",...} | |
| | |
Subscription Topics
Clients subscribe to specific event topics:
Topic Pattern:
customer_id:<id>:<resource>:<resource_id>
Examples:
o customer_id:123:call:*
-> All calls for customer 123
o customer_id:123:call:call-789
-> Specific call updates
o customer_id:123:agent:agent-456
-> Specific agent updates
o customer_id:123:queue:*
-> All queues for customer
o customer_id:123:conference:conf-999
-> Specific conference updates
WebSocket Use Cases
WebSocket Applications:
Agent Dashboard:
+--------------------------------------+
| o Real-time call notifications |
| o Queue status updates |
| o Agent presence |
| o Live chat messages |
+--------------------------------------+
Customer Portal:
+--------------------------------------+
| o Call status updates |
| o Campaign progress |
| o Billing updates |
| o System notifications |
+--------------------------------------+
Media Streaming:
+--------------------------------------+
| o Bi-directional audio (RTP) |
| o Live transcription feed |
| o Real-time metrics |
+--------------------------------------+
Connection Management
WebSocket Lifecycle:
+------------+
| Connect | Client establishes WebSocket
+------+-----+
|
v
+------------+
| Authenticate| Validate JWT token
+------+-----+
|
v
+------------+
| Subscribe | Client subscribes to topics
+------+-----+
|
v
+------------+
| Active | Bi-directional communication
| | o Server pushes events
| | o Client sends commands
| | o Pinger sends ping frames
+------+-----+
|
| (Keep-alive ping/pong)
|
v
+------------+
| Disconnect | Connection closed
+------------+
Keep-Alive Mechanism (Server-Side Ping/Pong)
VoIPBIN implements server-side keep-alive to prevent load balancer timeouts:
Keep-Alive Configuration:
+------------------------------------------------+
| Ping Interval: 30 seconds |
| Pong Wait: 60 seconds |
| Write Timeout: 10 seconds |
+------------------------------------------------+
Keep-Alive Flow:
Server Client
| |
| Every 30s: Send Ping Frame |
+---------------------------------------->>
| |
| Automatic Pong Response |
<<----------------------------------------+
| |
| Reset read deadline (60s) |
| |
Error Detection:
+------------------------------------------------+
| No pong within 60s -> Connection dead |
| Write failure -> Connection broken |
| Either error -> Close and cleanup |
+------------------------------------------------+
Keep-Alive Benefits:
Prevents Idle Drops: Load balancers see regular traffic
Dead Connection Detection: Server detects unresponsive clients
Automatic Cleanup: Zombie connections closed promptly
RFC 6455 Compliant: Uses standard WebSocket ping/pong frames
Connection Features:
Keepalive: Server-side ping every 30 seconds
Dead Detection: 60-second timeout for pong response
Auto-Reconnect: Client should reconnect on disconnect
Subscription Restore: Re-subscribe after reconnect
Write Protection: Mutex prevents concurrent write race conditions
Message Reliability
Different patterns provide different reliability guarantees:
Reliability Comparison:
Pattern Delivery Persistence Use Case
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
RabbitMQ RPC Exactly-once Yes Critical ops
(request-reply)
RabbitMQ Pub/Sub At-least-once Yes Important events
(may duplicate)
ZeroMQ Pub/Sub Best-effort No Real-time updates
(may lose)
WebSocket Best-effort No Client notifications
(may lose)
Reliability Patterns
Ensuring Reliability:
Critical Operations (RabbitMQ RPC):
+------------------------------------+
| o Persistent messages |
| o Manual acknowledgment |
| o Automatic retry |
| o Timeout handling |
| o Idempotent operations |
+------------------------------------+
Important Events (RabbitMQ Pub/Sub):
+------------------------------------+
| o Persistent messages |
| o Multiple subscribers |
| o Redundant processing OK |
| o Deduplication in subscriber |
+------------------------------------+
Real-Time Updates (ZeroMQ):
+------------------------------------+
| o No persistence |
| o Fast delivery |
| o Acceptable loss |
| o Often duplicated in RabbitMQ |
+------------------------------------+
Message Ordering
VoIPBIN guarantees ordering within specific boundaries:
Ordering Guarantees:
Same Queue: Different Queues:
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| Message 1| | Message 1| | Message 2|
+-----+----+ +-----+----+ +-----+----+
| | |
| Queue A | Queue A | Queue B
| | |
v v v
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| Message 2| | Service A| | Service B|
+-----+----+ +----------+ +----------+
| | |
| | May arrive in any order
v v v
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+
| Message 3| | Ordered | | No order |
+----------+ | delivery | | guarantee|
+----------+ +----------+
Ordered [x] Unordered [ ]
Ordering Strategy:
Within Queue: Messages delivered in order to same consumer
Across Queues: No ordering guarantee
Single Publisher: Maintains order if using single connection
Application Logic: Handle out-of-order messages when necessary
Error Handling and Retries
VoIPBIN implements comprehensive error handling:
Retry Strategy
Exponential Backoff Retry:
Attempt Delay Total Time
──────────────────────────────────
1 0s 0s
2 1s 1s
3 2s 3s
4 4s 7s
5 8s 15s
6 16s 31s
7 32s 63s
Max: 7 attempts, ~1 minute total
Dead Letter Queue
Failed messages move to dead letter queue for investigation:
Dead Letter Processing:
Normal Flow: Failed Flow:
+----------+ +----------+
| Message | | Message |
+-----+----+ +-----+----+
| |
| Process | Process (fails)
v v
+----------+ +----------+
| Success | | Retry |
+----------+ +-----+----+
| (max retries exceeded)
v
+----------+
| DLQ | Dead Letter Queue
+-----+----+
|
| Manual investigation
| or automated recovery
v
+----------+
| Alert |
+----------+
Error Categories
Error Handling by Type:
Transient Errors (Retry):
o Network timeout
o Database connection lost
o Service temporarily unavailable
-> Retry with exponential backoff
Permanent Errors (Don't Retry):
o Invalid data format
o Resource not found
o Permission denied
-> Send to DLQ, alert operator
Business Errors (Log and Return):
o Insufficient balance
o Invalid phone number
o Duplicate request
-> Return error to caller
Performance Optimization
VoIPBIN optimizes messaging performance:
Connection Pooling
Connection Management:
Service Instance
+------------------------------------+
| |
| Connection Pool (5 connections) |
| +----+ +----+ +----+ +----+ +----+|
| | 1 | | 2 | | 3 | | 4 | | 5 ||
| +-+--+ +-+--+ +-+--+ +-+--+ +-+--+|
| | | | | | |
+----+------+------+------+------+---+
| | | | |
+------+------+------+------+
|
| Single TCP connection
v
+----------+
| RabbitMQ |
+----------+
Reuse Connections: Don’t create per-request
Multiple Channels: Use channels for concurrency
Connection Limits: Pool size based on load
Health Checks: Monitor connection health
Batch Processing
For high-volume operations:
Batch vs Individual:
Individual Messages: Batch Processing:
+----+ +----+ +----+ +--------------+
| M1 | | M2 | | M3 | | M1, M2, M3 |
+-+--+ +-+--+ +-+--+ | M4, M5, M6 |
| | | | ... (100) |
v v v +------+-------+
Send 100 times Send once
(high overhead) (low overhead)
Bulk Publishing: Send multiple messages at once
Bulk ACK: Acknowledge multiple messages together
Reduced Overhead: Fewer network round-trips
Higher Throughput: 10x-100x improvement
Monitoring and Debugging
VoIPBIN monitors all communication channels:
Metrics
Message Queue Metrics:
Queue Depth:
+---------------------------------+
| Pending Messages |
| +--++--++--++--++--+ |
| |M1||M2||M3||M4||M5|... |
| +--++--++--++--++--+ |
+---------------------------------+
Alert if > 1000 messages
Processing Rate:
Messages/sec: ======== 850/s
Target: ======== 1000/s
Alert if < 500/s
Error Rate:
Failures: == 2%
Target: == < 5%
Alert if > 10%
Distributed Tracing
Track requests across services:
Trace ID: trace-123
1. API Gateway [50ms]
+- Authenticate [5ms]
+- Authorize [10ms]
+- Send RPC [35ms]
|
v
2. Call Manager [80ms]
+- Validate [10ms]
+- Create Record [20ms]
+- Initiate Call [50ms]
|
v
3. RTC Manager [120ms]
+- Setup Media [120ms]
Total: 250ms
Correlation IDs: Track requests across services
Timing: Measure latency at each hop
Errors: Identify where failures occur
Dependencies: Visualize service interactions
Best Practices
Message Design:
Keep messages small (<1MB)
Use JSON for human-readable format
Include timestamps for debugging
Add correlation IDs for tracing
Error Handling:
Always handle errors gracefully
Implement retry with exponential backoff
Use dead letter queues for failed messages
Alert on high error rates
Performance:
Use connection pooling
Batch messages when possible
Set appropriate timeouts
Monitor queue depths
Security:
Encrypt sensitive data in messages
Validate all incoming messages
Use authentication for connections
Limit message size to prevent abuse
Data Architecture
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s data layer: shared MySQL database (schema organization, common table patterns, migrations via Alembic), Redis cache (cache-aside pattern, key naming, TTL strategies), and session management. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand database schema conventions, caching strategies, data consistency models, or backup/recovery procedures.
VoIPBIN uses a shared data layer with MySQL for persistent storage and Redis for caching and session management. This architecture provides consistency across services while enabling high-performance data access.
Data Layer Overview
VoIPBIN’s data architecture consists of three layers:
Data Architecture:
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| Application Layer |
| (30+ Microservices) |
+--------------------+-------------------+----------------+
| |
| |
+---------------v------+ +--------v-----------+
| | | |
| Redis Cache | | MySQL Database |
| (Hot Data) | | (Persistent) |
| | | |
| o Sessions | | o All entities |
| o Frequently read | | o Relationships |
| o Temporary data | | o Audit logs |
| | | |
+----------------------+ +--------------------+
Cache-Aside Pattern:
1. Check cache first
2. If miss, query database
3. Store in cache for next time
MySQL Database
VoIPBIN uses a single shared MySQL database accessed by all services.
Database Characteristics
Shared Database Pattern:
+--------------+ +--------------+ +--------------+
| Service A | | Service B | | Service C |
| | | | | |
| call-mgr | | flow-mgr | | agent-mgr |
+------+-------+ +------+-------+ +------+-------+
| | |
| Connection | |
| Pooling | |
+--------+--------+-----------------+
|
v
+----------------------------+
| MySQL Database |
| |
| +----------------------+ |
| | calls table | |
| | conferences table | |
| | agents table | |
| | flows table | |
| | customers table | |
| | ... 100+ tables | |
| +----------------------+ |
+----------------------------+
Shared Schema: All services access same database
Logical Separation: Services own specific tables
ACID Transactions: Strong consistency guarantees
Connection Pooling: Each service maintains pool
Schema Organization
Tables are logically grouped by domain:
Table Organization:
Communication Domain:
o calls - Call records
o conferences - Conference bridges
o sms - SMS messages
o chats - Chat messages
o emails - Email records
Workflow Domain:
o flows - Call flow definitions
o flow_actions - Flow action steps
o queues - Call queues
o campaigns - Campaign definitions
Management Domain:
o customers - Customer accounts
o agents - Agent records
o billings - Billing records
o webhooks - Webhook configurations
o accesskeys - API keys
Resource Domain:
o numbers - Phone numbers
o recordings - Call recordings
o transcribes - Transcription jobs
o transcripts - Transcript segments
Common Table Pattern
All tables follow a consistent structure:
Standard Table Schema:
CREATE TABLE resource (
id VARCHAR(36) PRIMARY KEY, -- UUID
customer_id VARCHAR(36) NOT NULL, -- Ownership
-- Resource-specific fields
name VARCHAR(255),
status VARCHAR(50),
detail TEXT,
-- Timestamps
tm_create DATETIME(6) NOT NULL, -- Creation time
tm_update DATETIME(6) NOT NULL, -- Last update
tm_delete DATETIME(6) NOT NULL, -- Soft delete
-- Indexes
INDEX idx_customer (customer_id),
INDEX idx_status (status),
INDEX idx_tm_create (tm_create),
INDEX idx_tm_delete (tm_delete)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
Key Design Patterns:
UUID Primary Keys: Globally unique identifiers
Customer Ownership: Every resource has customer_id
Soft Deletes: tm_delete = ‘9999-01-01’ for active records
Microsecond Timestamps: DATETIME(6) for precise ordering
UTF8MB4: Full Unicode support including emojis
Data Access Patterns
Services access data through consistent patterns:
Data Access Flow:
Service Handler
|
| 1. Validate Input
v
+----------------------+
| Business Logic |
+------+---------------+
| 2. Check Cache
v
+----------------------+
| Cache Handler |
| (Redis) |
+------+---------------+
| Cache Miss
| 3. Query DB
v
+----------------------+
| DB Handler |
| (MySQL) |
+------+---------------+
| 4. Store in Cache
v
+----------------------+
| Return Result |
+----------------------+
Transaction Handling
VoIPBIN uses transactions for consistency:
Transaction Example:
BEGIN TRANSACTION
|
| 1. Create Call Record
+--> INSERT INTO calls ...
|
| 2. Update Customer Stats
+--> UPDATE customers SET total_calls = total_calls + 1 ...
|
| 3. Create Billing Entry
+--> INSERT INTO billings ...
|
| If all succeed:
| COMMIT
| If any fails:
| ROLLBACK
|
END TRANSACTION
ACID Guarantees: Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, Durable
Rollback on Error: All changes reverted if any step fails
Isolation Levels: READ COMMITTED for most operations
Lock Timeout: 30 seconds to prevent deadlocks
Query Optimization
VoIPBIN optimizes queries for performance:
Query Optimization Strategies:
1. Proper Indexing:
+---------------------------------+
| INDEX idx_customer_status |
| ON calls (customer_id, status) |
+---------------------------------+
SELECT * FROM calls
WHERE customer_id = ? AND status = 'active'
-> Uses index, fast lookup
2. Avoid SELECT *:
+---------------------------------+
| SELECT id, status, tm_create |
| FROM calls WHERE ... |
+---------------------------------+
-> Only retrieve needed columns
3. Pagination:
+---------------------------------+
| SELECT * FROM calls |
| WHERE customer_id = ? |
| LIMIT 50 OFFSET 0 |
+---------------------------------+
-> Limit result size
4. Connection Pooling:
+---------------------------------+
| Pool Size: 10-50 connections |
| Max Idle: 5 minutes |
| Max Lifetime: 1 hour |
+---------------------------------+
-> Reuse connections
Database Migrations
Schema changes are managed through Alembic migrations:
Migration Workflow:
Development Migration Script Production
| | |
| 1. Schema Change | |
| Needed | |
v | |
+-------------+ | |
| Create | | |
| Migration |------------------>| |
| Script | | |
+-------------+ | |
| | |
| 2. Test Locally | |
v | |
+-------------+ | |
| Run | | |
| Migration |<------------------| |
| (dev DB) | | |
+-------------+ | |
| | |
| 3. Commit to Git | |
v | |
+-------------+ | |
| Code Review | | |
| & Approval | | |
+-------------+ | |
| | |
| 4. Deploy | |
| | 5. Manual Execution |
| | (by human) |
| +-------------------------->>
| | |
| | alembic upgrade head |
| | |
Migration Best Practices:
Version Control: All migrations in git
Forward Only: Never modify existing migrations
Backward Compatible: Support gradual rollout
Manual Execution: Humans run migrations, not automation
Testing: Test on staging before production
Redis Cache
Redis provides fast access to frequently used data:
Cache Architecture
Redis Cache Pattern:
Application Request
|
| 1. Generate Cache Key
| key = "call:123"
v
+--------------------+
| Check Redis |
| GET call:123 |
+----+---------------+
|
+- Cache Hit --------+
| |
| v
| +----------------+
| | Return Cached |
| | Data (fast) |
| +----------------+
|
+- Cache Miss -------+
| |
| v
| +----------------+
| | Query MySQL |
| +----+-----------+
| |
| v
| +----------------+
| | Store in Redis |
| | SET call:123 |
| | EX 300 (5 min) |
| +----+-----------+
| |
| v
| +----------------+
| | Return Data |
| +----------------+
Cache Key Patterns
VoIPBIN uses structured cache keys:
Key Naming Convention:
<resource>:<id>[:<field>]
Examples:
o call:abc-123 -> Full call record
o agent:xyz-789:status -> Agent status only
o customer:customer-456 -> Customer record
o queue:queue-999:stats -> Queue statistics
o flow:flow-111:definition -> Flow definition
Advantages:
o Predictable keys
o Easy to invalidate
o Pattern matching for bulk operations
Data Structures
Redis supports multiple data structures:
Redis Data Structures:
1. String (Simple Values):
SET call:123:status "active"
GET call:123:status
-> "active"
2. Hash (Object Fields):
HSET call:123 status "active" duration "120"
HGET call:123 status
-> "active"
HGETALL call:123
-> {"status": "active", "duration": "120"}
3. List (Ordered Collection):
LPUSH queue:456:waiting call:123
LPUSH queue:456:waiting call:789
LRANGE queue:456:waiting 0 -1
-> [call:789, call:123]
4. Set (Unique Collection):
SADD conference:999:participants agent:111
SADD conference:999:participants agent:222
SMEMBERS conference:999:participants
-> [agent:111, agent:222]
5. Sorted Set (Scored Collection):
ZADD leaderboard 100 agent:111
ZADD leaderboard 95 agent:222
ZRANGE leaderboard 0 -1 WITHSCORES
-> [(agent:111, 100), (agent:222, 95)]
Cache Expiration
All cached data has Time-To-Live (TTL):
TTL Strategy:
Data Type TTL Reason
─────────────────────────────────────────────
Session tokens 1 hour Security
User profiles 5 min Frequently updated
Call records 1 min Real-time changes
Configuration 1 hour Rarely changes
Static data 24 hours Almost never changes
Set TTL:
SET key value EX 300 # 5 minutes
SETEX key 300 value # Same as above
EXPIRE key 300 # Set TTL on existing key
Cache Invalidation
VoIPBIN invalidates cache on updates:
Cache Invalidation Flow:
Update Request
|
| 1. Update Database
v
+--------------------+
| UPDATE calls |
| SET status='ended'|
| WHERE id='123' |
+----+---------------+
|
| 2. Invalidate Cache
v
+--------------------+
| DEL call:123 |
+----+---------------+
|
| 3. Return Success
v
+--------------------+
| Response to Client|
+--------------------+
Next Read:
o Cache miss
o Fetch from DB
o Store in cache with new data
Cache Patterns
Common Cache Patterns:
1. Cache-Aside (Read Through):
App checks cache -> Cache miss -> Query DB -> Store in cache
2. Write-Through:
App writes to cache -> Cache writes to DB -> Return success
3. Write-Behind (Async):
App writes to cache -> Return success -> Cache writes to DB later
VoIPBIN primarily uses Cache-Aside for simplicity and consistency.
Session Management
Redis stores session data for authenticated users:
Session Structure
Session Data in Redis:
Key: session:<token-hash>
Type: Hash
TTL: 1 hour (refreshed on activity)
Data:
+-------------------------------------+
| customer_id : customer-123 |
| agent_id : agent-456 |
| permissions : ["admin", "call"] |
| login_time : 2026-01-20 12:00 |
| last_activity : 2026-01-20 12:30 |
| ip_address : 192.168.1.100 |
| user_agent : Mozilla/5.0 ... |
+-------------------------------------+
Session Lifecycle
Session Flow:
1. Login:
+----------------------------+
| Generate JWT token |
| Hash token -> session_key |
| Store session in Redis |
| SET session:xyz {...} |
| EXPIRE session:xyz 3600 |
+----------------------------+
2. Request:
+----------------------------+
| Extract token from header |
| Hash token -> session_key |
| GET session:xyz |
| Validate session data |
| EXPIRE session:xyz 3600 | <- Refresh TTL
+----------------------------+
3. Logout:
+----------------------------+
| Extract token from header |
| Hash token -> session_key |
| DEL session:xyz |
+----------------------------+
Data Consistency
VoIPBIN ensures consistency across data layers:
Consistency Model
Consistency Strategy:
Strong Consistency: Eventual Consistency:
+--------------+ +--------------+
| MySQL | | Redis |
| (Source of | | (May be |
| Truth) | | stale) |
+------+-------+ +------+-------+
| |
| Always consistent | May lag behind
| ACID transactions | Best effort
| |
+----------+---------------+
|
Database is authoritative
Write Path
Write Flow (Strong Consistency):
1. Write Request
|
v
2. Update Database First
+- BEGIN TRANSACTION
+- UPDATE table ...
+- COMMIT
|
v
3. Invalidate Cache
+- DEL cache_key
|
v
4. Publish Event
+- Notify subscribers
|
v
5. Return Success
Database updated before cache invalidation
ensures consistency.
Read Path
Read Flow (Eventual Consistency Acceptable):
1. Read Request
|
v
2. Check Cache
+- Cache Hit -> Return (may be slightly stale)
+- Cache Miss -> Continue
|
v
3. Query Database
+- SELECT * FROM table WHERE ...
|
v
4. Store in Cache
+- SET cache_key value EX ttl
|
v
5. Return Result
Data Backup and Recovery
VoIPBIN implements comprehensive backup strategy:
Backup Architecture
Backup Strategy:
Production Database
|
| Continuous Replication
v
+--------------------+
| Read Replica | <- Used for backups
+----+---------------+ (no production impact)
|
| Daily Full Backup
v
+--------------------+
| Backup Storage |
| (Google Cloud) |
| |
| o Daily: 30 days |
| o Weekly: 1 year |
| o Monthly: 7 years|
+--------------------+
Backup Schedule
Backup Timeline:
Daily (3 AM UTC):
+------------------------------+
| Full database dump |
| Stored for 30 days |
| ~100 GB compressed |
+------------------------------+
Weekly (Sunday 3 AM):
+------------------------------+
| Full database dump |
| Stored for 1 year |
| Long-term retention |
+------------------------------+
Continuous:
+------------------------------+
| Binary logs (point-in-time) |
| Stored for 7 days |
| For recovery between backups |
+------------------------------+
Recovery Procedures
Recovery Scenarios:
1. Recent Data Loss (< 7 days):
+----------------------------+
| Restore latest daily backup|
| Apply binary logs |
| Point-in-time recovery |
+----------------------------+
Recovery time: 1-2 hours
2. Older Data Loss (< 1 year):
+----------------------------+
| Restore weekly backup |
| No binary logs available |
+----------------------------+
Recovery time: 2-4 hours
3. Disaster Recovery:
+----------------------------+
| Failover to replica |
| Promote to primary |
| Restore from backup |
+----------------------------+
Recovery time: 15 minutes
Performance Monitoring
VoIPBIN monitors data layer performance:
Database Metrics
Key Database Metrics:
Query Performance:
+-------------------------------------+
| Slow queries (> 1 second): 0.1% |
| Average query time: 5ms |
| P95 query time: 50ms |
| P99 query time: 200ms |
+-------------------------------------+
Connection Pool:
+-------------------------------------+
| Active connections: 45/50 |
| Idle connections: 5/50 |
| Wait time: < 1ms |
+-------------------------------------+
Table Size:
+-------------------------------------+
| calls: 50 million rows |
| conferences: 5 million rows |
| agents: 10,000 rows |
| Total size: 500 GB |
+-------------------------------------+
Cache Metrics
Redis Performance:
Hit Rate:
+-------------------------------------+
| Cache hits: 95% |
| Cache misses: 5% |
| Target: > 90% |
+-------------------------------------+
Memory Usage:
+-------------------------------------+
| Used memory: 8 GB / 16 GB |
| Peak memory: 12 GB |
| Eviction: LRU policy |
+-------------------------------------+
Latency:
+-------------------------------------+
| P50: 0.5ms |
| P95: 2ms |
| P99: 5ms |
+-------------------------------------+
Scalability Considerations
As VoIPBIN scales, data layer adapts:
Database Scaling
Scaling Strategy:
Current (< 1M customers):
+--------------------------+
| Single Primary |
| + Read Replicas (3) |
+--------------------------+
Future (> 1M customers):
+--------------------------+
| Sharding by Customer |
| |
| Shard 1: customers A-M |
| Shard 2: customers N-Z |
+--------------------------+
Cache Scaling
Redis Scaling:
Current:
+--------------------------+
| Single Redis Instance |
| 16 GB Memory |
+--------------------------+
Future:
+--------------------------+
| Redis Cluster |
| o Multiple nodes |
| o Automatic sharding |
| o High availability |
+--------------------------+
Best Practices
Database:
Use indexes for all WHERE clauses
Avoid SELECT *, specify columns
Use connection pooling
Set appropriate timeouts
Monitor slow queries
Regular ANALYZE TABLE for statistics
Cache:
Set appropriate TTLs
Invalidate on updates
Use structured keys
Monitor hit rates
Handle cache failures gracefully
Don’t store large objects (> 1MB)
Security:
Use parameterized queries (prevent SQL injection)
Encrypt sensitive data at rest
Use SSL/TLS for connections
Rotate database credentials regularly
Audit database access
Restrict network access
Monitoring:
Track query performance
Monitor connection pool utilization
Alert on cache hit rate < 90%
Alert on slow queries
Monitor disk space
Track replication lag
Data Flow Diagrams
Note
AI Context
This page illustrates end-to-end data flows through VoIPBIN for common operations: API request lifecycle, event publishing, WebSocket real-time updates, media streaming (audio pipeline), database write patterns, campaign execution, transcription, and webhook delivery. Relevant when an AI agent needs to trace how a request moves through the system or understand data transformations at each stage.
This section illustrates how data flows through VoIPBIN’s components for common operations. Understanding these flows helps developers integrate with the platform and troubleshoot issues.
End-to-End Request Flow
Every API request follows a consistent path through the system:
Complete API Request Flow:
Client Load Balancer API Gateway Backend Service Database
| | | | |
| HTTPS Request | | | |
+---------------->| | | |
| | TLS Termination | | |
| +----------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | | 1. Parse Auth | |
| | | Header | |
| | | | |
| | | 2. Validate JWT | |
| | | or AccessKey | |
| | | | |
| | | 3. Extract | |
| | | customer_id | |
| | | | |
| | | 4. RabbitMQ RPC | |
| | +----------------->| |
| | | | |
| | | | 5. Check Redis |
| | | | Cache |
| | | +------------------>|
| | | | |
| | | |<------------------+
| | | | (cache hit/miss) |
| | | | |
| | | | 6. Query MySQL |
| | | | (if cache miss)|
| | | +------------------>|
| | | | |
| | | |<------------------+
| | | | Data |
| | | | |
| | | | 7. Update Cache |
| | | +------------------>|
| | | | |
| | |<-----------------+ |
| | | RPC Response | |
| | | | |
| | | 8. Check | |
| | | Authorization | |
| | | (customer_id) | |
| | | | |
|<----------------+-----------------+ | |
| JSON Response | | | |
| | | | |
Key Data Transformations:
Data Format at Each Stage:
1. Client -> API Gateway:
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: HTTPS/JSON |
| Auth: Bearer JWT or AccessKey header |
| Body: JSON request body |
+------------------------------------------+
2. API Gateway -> Backend Service:
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: RabbitMQ message (JSON) |
| Contains: customer_id, agent_id, |
| original request data |
| Queue: bin-manager.<service>.request |
+------------------------------------------+
3. Backend Service -> Database:
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: SQL queries (parameterized) |
| ORM: Squirrel query builder |
+------------------------------------------+
4. Backend Service -> API Gateway:
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: RabbitMQ response (JSON) |
| Contains: status_code, data, error |
+------------------------------------------+
5. API Gateway -> Client:
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: HTTPS/JSON |
| Headers: Content-Type, Cache-Control |
+------------------------------------------+
Event Publishing Flow
When resources change, events propagate through the system:
Event Publishing Flow:
Source Service RabbitMQ Exchange Subscriber Services
| | |
| 1. Business Logic | |
| (e.g., call ends)| |
| | |
| 2. Update Database | |
| | |
| 3. Invalidate Cache | |
| | |
| 4. Publish Event | |
+-------------------->| |
| Exchange: | |
| call.events | |
| | |
| | 5. Fanout to Queues |
| +----------+-------------+
| | | |
| v v v
| +--------+ +--------+ +--------+
| |billing | |webhook | |queue |
| |.call | |.call | |.call |
| |.events | |.events | |.events |
| +---+----+ +---+----+ +---+----+
| | | |
| | 6. Process |
| | Event |
| v v v
| billing- webhook- queue-
| manager manager manager
| | | |
| | 7. Take | 7. Send | 7. Update
| | Action| Webhook | Stats
| | | |
Event Data Structure:
Published Event:
Exchange: call.events
Routing Key: call.hungup
Message:
{
"event_id": "uuid",
"event_type": "call_hungup",
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"customer_id": "uuid",
"resource": {
"id": "uuid",
"type": "call",
"source": "+15551234567",
"destination": "+15559876543",
"duration": 120,
"status": "completed",
"hangup_cause": "normal_clearing"
}
}
Subscriber Processing:
Event Processing by Service:
billing-manager:
+------------------------------------------+
| On: call_hungup |
| Action: |
| 1. Calculate call cost |
| 2. Deduct from customer balance |
| 3. Create billing record |
+------------------------------------------+
webhook-manager:
+------------------------------------------+
| On: call_hungup |
| Action: |
| 1. Lookup customer webhook config |
| 2. Format webhook payload |
| 3. POST to customer endpoint |
| 4. Handle retries on failure |
+------------------------------------------+
queue-manager:
+------------------------------------------+
| On: call_hungup |
| Action: |
| 1. Check if call was from queue |
| 2. Update queue statistics |
| 3. Mark agent as available |
+------------------------------------------+
Real-Time Data Flow (WebSocket)
WebSocket connections provide real-time updates to clients:
WebSocket Data Flow:
Client API Gateway ZMQ Publisher Backend Service
| | | |
| 1. WS Connect | | |
+----------------->| | |
| | 2. Authenticate | |
| | (JWT token) | |
| | | |
| 3. Subscribe | | |
| {"type":"subscribe", | |
| "topics":["customer_id:123:call:*"]} | |
+----------------->| | |
| | 4. Register | |
| | Subscription | |
| | | |
| | | | 5. Call Starts
| | | | (business event)
| | | |
| | |<---------------------+
| | | 6. ZMQ Publish |
| | | topic: call.state |
| | | |
| |<-------------------+ |
| | 7. Match to | |
| | Subscriptions | |
| | | |
|<-----------------+ | |
| 8. Push Event | | |
| {"event":"call_created",...} | |
| | | |
Topic Matching:
Subscription Topic Matching:
Subscribed Topic:
customer_id:123:call:*
Matches:
+------------------------------------------+
| customer_id:123:call:abc-456 [match] |
| customer_id:123:call:xyz-789 [match] |
| customer_id:123:call:* [match] |
+------------------------------------------+
Does Not Match:
+------------------------------------------+
| customer_id:456:call:abc-123 [no match] |
| customer_id:123:conference:* [no match] |
+------------------------------------------+
Media Stream Data Flow
Audio data flows through the media pipeline:
Audio Stream Flow (AI Voice):
Caller RTPEngine Asterisk pipecat-mgr AI/LLM
| | | | |
| RTP Audio | | | |
| (Various) | | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | Transcode | | |
| | to ulaw | | |
| +------------>| | |
| | | Audiosocket | |
| | | (8kHz ulaw) | |
| | +-------------->| |
| | | | |
| | | | Resample to |
| | | | 16kHz PCM |
| | | | |
| | | | WebSocket |
| | | | (Protobuf) |
| | | +-------------->|
| | | | |
| | | | | STT +
| | | | | LLM +
| | | | | TTS
| | | | |
| | | |<--------------+
| | | | Audio Response|
| | | | |
| | | | Resample to |
| | | | 8kHz ulaw |
| | | | |
| | |<--------------+ |
| | | Audiosocket | |
| | | | |
| |<------------+ | |
| | RTP | | |
|<-------------+ | | |
| Audio to | | | |
| Caller | | | |
Audio Format Transformations:
Audio Format Pipeline:
External (Varies)
+------------------------------------------+
| Codecs: G.711, G.722, Opus, etc. |
| Sample Rate: 8kHz - 48kHz |
| Bitrate: 64kbps - 510kbps |
+------------------------------------------+
|
| RTPEngine (Edge Transcoding)
v
Internal (Standard)
+------------------------------------------+
| Codec: G.711 ulaw |
| Sample Rate: 8kHz |
| Bitrate: 64kbps |
+------------------------------------------+
|
| pipecat-manager (AI Processing)
v
AI Pipeline
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: PCM Linear |
| Sample Rate: 16kHz |
| Bit Depth: 16-bit |
+------------------------------------------+
Database Write Flow
Write operations follow a specific pattern for consistency:
Database Write Flow:
Service Handler Cache Handler DB Handler MySQL
| | | |
| 1. Validate | | |
| Input | | |
| | | |
| 2. Business | | |
| Logic | | |
| | | |
| 3. Call DB Handler| | |
+---------------------------------->| |
| | | |
| | | 4. Begin |
| | | Transaction
| | +------------->|
| | | |
| | | 5. INSERT/ |
| | | UPDATE |
| | +------------->|
| | | |
| | |<-------------+
| | | Success |
| | | |
| | | 6. COMMIT |
| | +------------->|
| | | |
| |<----------------+ |
| | Return ID | |
| | | |
| | 7. Invalidate | |
| | Cache | |
|<------------------+ | |
| | DEL key | |
| | | |
| 8. Publish Event | | |
| (RabbitMQ) | | |
| | | |
Write Consistency Rules:
Data Consistency:
Order of Operations:
+------------------------------------------+
| 1. Write to database FIRST |
| 2. Invalidate cache SECOND |
| 3. Publish event THIRD |
+------------------------------------------+
Why This Order:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Database is source of truth |
| o Cache invalidation ensures freshness |
| o Events notify other services |
| o If publish fails, data still correct |
+------------------------------------------+
Failure Handling:
+------------------------------------------+
| DB write fails -> Rollback, return error|
| Cache inv. fails-> Log, continue |
| Event pub. fails-> Log, retry async |
+------------------------------------------+
Campaign Execution Data Flow
Outbound campaigns involve complex data orchestration:
Campaign Data Flow:
Scheduler campaign-mgr outdial-mgr MySQL call-mgr
| | | | |
| 1. Trigger | | | |
| Campaign | | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | | | |
| | 2. Get | | |
| | Campaign | | |
| +------------------------------>| |
| | | | |
| |<------------------------------+ |
| | Campaign Data | | |
| | | | |
| | 3. Get Next | | |
| | Targets | | |
| +-------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | | 4. Query | |
| | | Outplan | |
| | +-------------->| |
| | | | |
| | |<--------------+ |
| | | Target List | |
| | | | |
| |<--------------+ | |
| | Dial Targets | | |
| | | | |
| | 5. For each target: | |
| | +-------------------------------------------+ |
| | | | | |
| | | Create Call | | |
| | +-------------------------------------------->|
| | | | | |
| | | |<------------+ |
| | | | Call Created| |
| | | | | |
| | +-------------------------------------------+ |
| | | | |
| | 6. Subscribe | | |
| | call_hungup| | |
| | | | |
| | | |
| | (Later) | | |
| | 7. Event: | | |
| | call_hungup| | |
| |<---------------------------------------------|
| | | | |
| | 8. Update | | |
| | Campaign | | |
| | Status | | |
| +------------------------------>| |
| | | | |
Campaign State Machine:
Campaign Data States:
Campaign Record:
+------------------------------------------+
| status: pending -> running -> completed |
| total_targets: 1000 |
| dialed: 0 -> 500 -> 1000 |
| answered: 0 -> 250 -> 500 |
| failed: 0 -> 50 -> 100 |
+------------------------------------------+
Outplan (Dial Target):
+------------------------------------------+
| status: pending -> dialing -> completed |
| dial_count: 0 -> 1 -> 2 |
| last_dial_time: timestamp |
| result: null -> answered/busy/no_answer |
+------------------------------------------+
Transcription Data Flow
Real-time transcription processes audio streams:
Transcription Data Flow:
Asterisk call-mgr transcribe-mgr STT Provider MySQL
| | | | |
| Channel | | | |
| Up | | | |
+------------>| | | |
| | | | |
| | 1. Start | | |
| | Transcribe| | |
| +------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | | 2. Create | |
| | | Transcribe | |
| | | Record | |
| | +-------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | 3. Connect to | |
| | | STT Stream | |
| | +----------------->| |
| | | | |
| Audio | | | |
| Stream | | | |
+-------------------------->| | |
| | | Audio Chunks | |
| | +----------------->| |
| | | | |
| | | | 4. Process |
| | | | Audio |
| | | | |
| | |<-----------------+ |
| | | Transcript | |
| | | Segment | |
| | | | |
| | | 5. Save | |
| | | Transcript | |
| | +-------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | 6. Publish | |
| | | Event | |
| | | (transcript_created) |
| | | | |
Transcript Data Structure:
Transcript Record:
transcribes table:
+------------------------------------------+
| id: uuid |
| customer_id: uuid |
| reference_type: "call" | "conference" |
| reference_id: uuid (call_id) |
| language: "en-US" |
| status: "running" | "completed" |
+------------------------------------------+
transcripts table (segments):
+------------------------------------------+
| id: uuid |
| transcribe_id: uuid |
| direction: "in" | "out" |
| message: "Hello, how can I help?" |
| tm_transcript: relative timestamp |
| tm_create: absolute timestamp |
+------------------------------------------+
Webhook Delivery Data Flow
Webhooks deliver events to external systems:
Webhook Delivery Flow:
Event Source webhook-mgr MySQL HTTP Client External
| | | | |
| Event: | | | |
| call_hungup | | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | | | |
| | 1. Lookup | | |
| | Webhook | | |
| | Config | | |
| +--------------->| | |
| | | | |
| |<---------------+ | |
| | Webhook URL, | | |
| | Secret | | |
| | | | |
| | 2. Format | | |
| | Payload | | |
| | | | |
| | 3. Sign | | |
| | Payload | | |
| | (HMAC-SHA256)| | |
| | | | |
| | 4. Create | | |
| | Delivery | | |
| | Record | | |
| +--------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | 5. POST | | |
| | Webhook | | |
| +------------------------------>| |
| | | | |
| | | +-------------->|
| | | | HTTPS POST |
| | | | |
| | | |<--------------+
| | | | 200 OK |
| | | | |
| |<------------------------------+ |
| | Success | | |
| | | | |
| | 6. Update | | |
| | Delivery | | |
| | Status | | |
| +--------------->| | |
| | | | |
Webhook Payload:
Webhook HTTP Request:
POST https://customer.example.com/webhook
Content-Type: application/json
X-VoIPBIN-Signature: sha256=abc123...
X-VoIPBIN-Timestamp: 2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z
X-VoIPBIN-Event: call_hungup
{
"id": "event-uuid",
"type": "call_hungup",
"created": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"data": {
"id": "call-uuid",
"customer_id": "customer-uuid",
"source": "+15551234567",
"destination": "+15559876543",
"duration": 120,
"status": "completed",
"hangup_cause": "normal_clearing"
}
}
Signature Verification (Customer Side):
Signature Verification:
1. Extract signature from header:
X-VoIPBIN-Signature: sha256=abc123...
2. Compute expected signature:
expected = HMAC-SHA256(
secret = "webhook_secret",
message = timestamp + "." + body
)
3. Compare:
if (signature == expected) {
// Valid webhook
} else {
// Reject - possible tampering
}
Data Synchronization Patterns
Services maintain data consistency through patterns:
Cache-Aside Pattern:
Service Redis MySQL
| | |
| 1. Get Call | |
+------------------>| |
| | |
| Cache Miss | |
|<------------------+ |
| | |
| 2. Query DB | |
+------------------------------------->|
| | |
|<-------------------------------------+
| Call Data | |
| | |
| 3. Store in Cache | |
| (TTL: 24 hours) | |
+------------------>| |
| | |
| 4. Return Data | |
| | |
Write-Through Pattern:
Service MySQL Redis
| | |
| 1. Update Call | |
+------------------>| |
| | |
|<------------------+ |
| Commit Success | |
| | |
| 2. Invalidate | |
| Cache | |
+------------------------------------->|
| | |
|<-------------------------------------+
| DEL Success | |
| | |
Event Sourcing (for Audit):
Service MySQL Audit Log
| | |
| 1. Action: | |
| Delete Call | |
| | |
| 2. Write to | |
| calls table | |
+------------------>| |
| | |
| 3. Write to | |
| audit_log | |
+------------------------------------->|
| | |
| Record: | |
| - action: delete | |
| - resource: call | |
| - actor: agent_id | |
| - timestamp | |
| - before_state | |
| | |
Real-Time Communication (RTC)
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s real-time communication stack: Kamailio (stateless SIP edge routing), Asterisk (three specialized farms for calls, conferences, and registration), RTPEngine (media proxy and codec transcoding), conference architecture, and SIP session recovery after Asterisk crashes. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand VoIP call flow mechanics, media handling, codec strategies, or high-availability features.
VoIPBIN’s RTC architecture handles all real-time voice and video communication through a distributed stack of specialized components. The architecture separates signaling (SIP) from media (RTP) processing, enabling independent scaling and fault tolerance.
VoIP Stack Overview
VoIPBIN’s VoIP stack consists of three main components working together:
SIP Traffic Flow:
External Client Internal Services
| |
| SIP (INVITE, etc.) |
v v
+----------+ +----------+ +------------------+
| Load | SIP | Kamailio | SIP | Asterisk |
| Balancer |<------->| Farm |<------->| (Call) |
+----------+ +-----+----+ +--------+---------+
| |
| RTP Control | RTP Control
v |
+----------+ |
| RTPEngine| |
| Farm |<-----------------+
+-----+----+ Media
|
| RTP (Audio/Video)
v
External Client
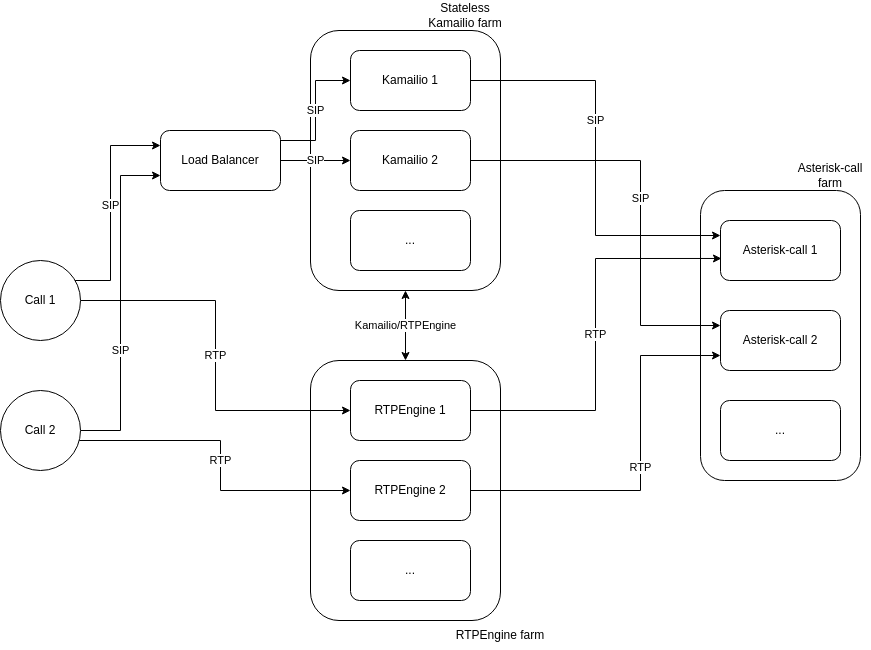
Key Characteristics:
Stateless SIP Proxies: Kamailio instances maintain no state, enabling dynamic scaling
Distributed Media Processing: RTPEngine handles all media transcoding and routing
Separated Concerns: Signaling (Kamailio) and media (RTPEngine, Asterisk) are independent
Zero-Downtime: Load balancer redirects traffic when instances fail
Horizontal Scaling: Add more instances of any component to handle increased load
Traffic Flow:
SIP Signaling: Load balancer distributes SIP traffic to Kamailio instances
Call Routing: Kamailio routes signaling to appropriate Asterisk instance
Media Setup: RTPEngine handles RTP media streams and transcoding
Call Control: Asterisk manages call state and conference bridges
This modular design ensures VoIPBIN can provide reliable, scalable VoIP services while accommodating high traffic loads.
Kamailio - SIP Edge Router
Kamailio is an open-source SIP server providing the edge routing layer for all SIP traffic.
Official Site: https://www.kamailio.org/
Role in VoIPBIN:
Kamailio acts as the stateless SIP proxy and edge router, responsible for:
SIP Routing: Forwarding SIP messages to appropriate backend services
Load Distribution: Balancing traffic across Asterisk instances
Authentication: Validating SIP registration credentials
Protocol Handling: Managing SIP message parsing and routing
Stateless Operation:
Client Kamailio-1 Kamailio-2 Asterisk
| | | |
| INVITE | | |
+---------------->| | |
| | Forward | |
| +---------------------------------->|
| | | |
| | | |
| 200 OK | | |
|<----------------+-----------------------------------+
| | | |
| ACK | | |
+---------------------------------->| |
| | | Forward |
| | +---------------->|
| | | |
Note: Different Kamailio instances handle different messages
in the same call (stateless operation)
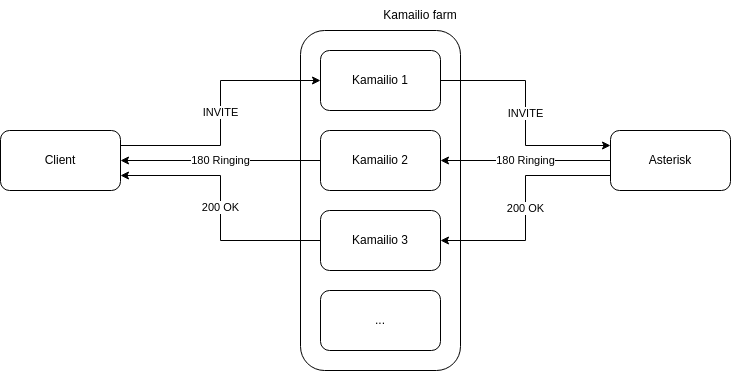
Key Features:
Load Balancing: Distributes incoming SIP traffic across multiple instances
Stateless Operation: No state maintained, enabling dynamic scaling and failover
High Availability: Instances can be added or removed without affecting ongoing calls
Fast Performance: C-based implementation with minimal overhead
Stateless Benefits:
In the diagram above, Kamailio receives initial SIP traffic from the client and forwards it to Asterisk. However, subsequent SIP messages in the same call may go to different Kamailio instances. This stateless design allows for:
Instant failover without session loss
Dynamic scaling without coordination
Simplified operations and deployment
Asterisk - Media and Call Processing
Asterisk is an open-source communications platform providing comprehensive telephony services.
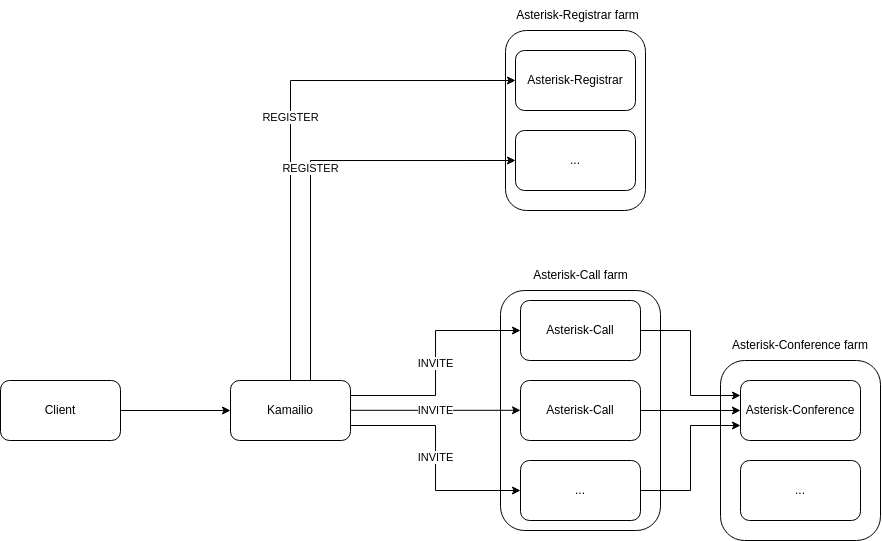
VoIPBIN’s Three Asterisk Farms:
VoIPBIN employs three specialized Asterisk farms for optimized scalability and fault isolation:
Asterisk Farm Architecture:
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| Kamailio Farm |
+------+-------------------------------------+------------+
| |
| All Calls | Registrations
v Conferences v
+-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
| Asterisk | | Asterisk | | Asterisk |
| Call | | Conference | | Registrar |
| Farm | | Farm | | Farm |
| |--->| | | |
| o 1:1 calls | | o N-way | | o SIP |
| o Call | | conference| | REGISTER |
| bridging | | o Mixing | | o Auth |
| o Transfers | | o Recording | | o Presence |
+-------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
1. Asterisk-Call Farm
Handles 1:1 call processing:
Call setup and teardown
Media bridging between two parties
Call transfers and forwarding
DTMF processing
Call recording
2. Asterisk-Conference Farm
Manages multi-party conference calls:
Conference bridge creation and management
Participant mixing (up to hundreds of participants)
Conference recording
Participant management (mute, kick, etc.)
Audio/video conferencing
3. Asterisk-Registrar Farm
Handles SIP registration:
User authentication
Registration lifecycle management
Presence information
Contact database
Farm Benefits:
Independent Scaling: Scale each farm based on specific load patterns
Fault Isolation: Issues in one farm don’t affect others
Optimized Configuration: Each farm can be tuned for its specific workload
Targeted Upgrades: Update farms independently without full system downtime
Inter-Farm Communication:
While farms operate independently, Asterisk-Call and Asterisk-Conference communicate when bridging calls into conference sessions, enabling seamless transitions from 1:1 calls to conferences.
RTPEngine - Media Proxy and Transcoding
RTPEngine is an open-source media proxy providing RTP processing and transcoding capabilities.
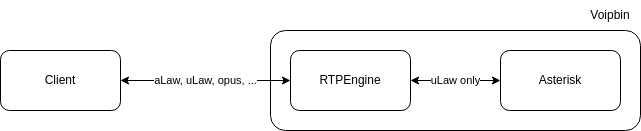
Role in VoIPBIN:
RTPEngine serves as the codec edge server and media proxy:
Codec Transcoding:
External Client VoIPBIN Internal
(Various Codecs) (ulaw only)
| |
| RTP (G.722, Opus, etc.) |
v v
+---------------------------------------------+
| RTPEngine Farm |
| |
| o Transcode external -> ulaw (internal) |
| o Transcode ulaw (internal) -> external |
| o NAT traversal |
| o Packet switching |
| o SRTP/RTP conversion |
+------------------+--------------------------+
|
| RTP (ulaw)
v
Asterisk Farm
Responsibilities:
Codec Transcoding: Convert between external codecs and internal ulaw
NAT Traversal: Handle media through NAT and firewalls
SRTP Support: Encrypt/decrypt media streams
Packet Routing: Efficient RTP packet switching
Load Distribution: Distribute media processing across instances
Internal Codec Strategy:
Internal: VoIPBIN uses ulaw codec exclusively for all internal communication
External: Clients can use any supported codec (G.711, G.722, Opus, etc.)
Edge Transcoding: RTPEngine performs all transcoding at the edge
Performance: Internal ulaw ensures minimal CPU overhead for media processing
This edge transcoding strategy ensures optimal internal performance while supporting diverse client codecs.
Conference Architecture
VoIPBIN’s conference functionality is powered by the dedicated Asterisk-Conference farm.
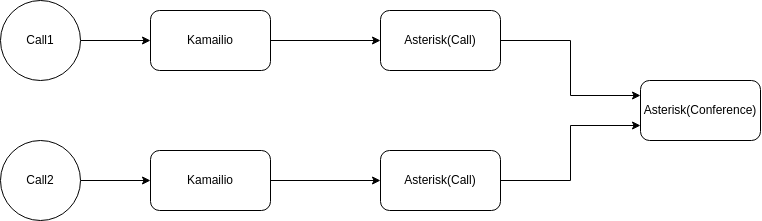
Conference Design:
VoIPBIN leverages a dedicated Asterisk-Conference component for all conference calls:
Advantages:
Isolation and Scalability: Conference processing separated from regular calls ensures stable service
Independent Scaling: Conference farm scales based on conferencing usage patterns
Centralized Management: All conference operations managed in one place
Fault Isolation: Conference issues don’t impact regular call processing
Conference Flow
Conference Lifecycle:
Flow Manager Asterisk-Conf Conference Bridge
| | |
| 1. Create Conf | |
+----------------->| |
| | 2. Create Bridge |
| +------------------->|
| | |
| 3. Add Part. 1 | |
+----------------->| 4. Join Bridge |
| +------------------->|
| | |
| 5. Add Part. 2 | |
+----------------->| 6. Join Bridge |
| +------------------->|
| | |
| | [Audio Mixing] |
| |<------------------>|
| | |
| 7. End Conf | |
+----------------->| 8. Destroy Bridge |
| +------------------->|
| | |
Conference Steps:
Call Initiation: Flow Manager requests conference creation (via “connect” or “conference_join” action)
Conference Establishment: Asterisk-Conference creates dedicated bridge for participants
Participant Joining: Participants added to bridge sequentially or simultaneously
Conference Interaction: Participants communicate with voice/video, screen sharing, etc.
Conference Termination: Bridge destroyed when conference ends or all participants leave
Conference Features:
Audio and video mixing
Recording capabilities
Dynamic participant management
Mute/unmute controls
Moderator capabilities
Entry/exit tones
1:1 Calls as Conferences
VoIPBIN treats 1:1 calls as special cases of conferencing with only two participants:
1:1 Call = Conference with 2 Participants
+--------------+ +--------------+
| Participant A| | Participant B|
+------+-------+ +------+-------+
| |
| Conference Bridge |
| (2 participants) |
+-----------+------------+
|
Asterisk-Call
(manages bridge)
Benefits of Unified Approach:
Simplified Development: Same infrastructure for 1:1 calls and conferences
Enhanced Flexibility: Seamless transitions from 1:1 to multi-party conferences
Improved Resource Utilization: Optimized resource allocation across all call types
Consistent Features: Same feature set available for all call types
Easier Maintenance: Single codebase for all call scenarios
Example Transition:
1:1 Call -> Multi-Party Conference:
Initial State: Add 3rd Party: Result:
+-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+
| A |--| B | | A |--| B | | A |--| B |
+-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+
| |
| |
v v
+-----+ +-----+
| C | | C |
+-----+ +-----+
2-participant bridge Add participant 3-participant bridge
(1:1 call) without disruption (conference)
SIP Session Recovery
VoIPBIN provides SIP session recovery to maintain active SIP sessions even when an Asterisk instance crashes unexpectedly. This feature prevents call drops, conference exits, and media failures by making the client perceive the session as uninterrupted.
How It Works
When an Asterisk instance crashes, all SIP sessions managed by that instance disappear immediately. Without a BYE message, clients experience unexpected termination. VoIPBIN recovers sessions through an automated process:
Session Recovery Flow:
Asterisk-1 Client Sentinel Call-manager HOMER DB Asterisk-2
| | | | | |
| Active | | | | |
| Session | | | | |
|<----------->| | | | |
| | | | | |
X CRASH | | | | |
| | | | |
| Detect Crash | | |
| | | | |
| Publish Crash event | | |
| +------------->| | |
| Query Sessions | |
| Get SIP Headers | |
| |<--------+ |
| | |
| Create Channels |
| +--------------------->|
| |
| |
| |
| Send Recovery INVITE |
|<--------------------------------------------------+
| |
| 200 OK (same Call-ID) |
+-------------------------------------------------->|
| |
Session | |
Recovered | |
|<------------------------------------------------->|
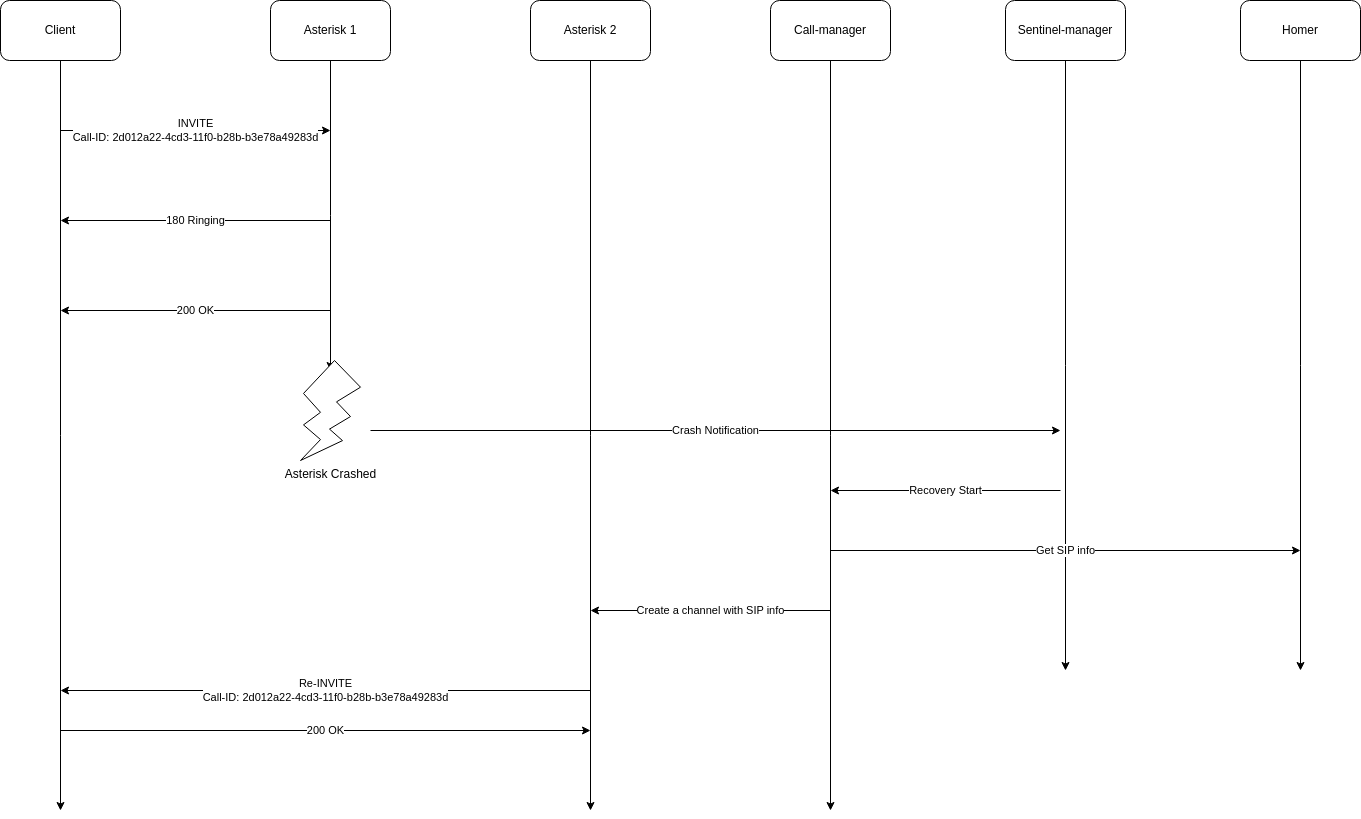
Detailed Steps
1. Crash Detection
The sentinel-manager quickly detects abnormal termination of an Asterisk instance.
2. Session Lookup
The internal database is queried to retrieve all active sessions from the failed instance.
3. SIP Field Collection (via HOMER)
The HOMER SIP capture API provides SIP header information:
Call-ID
From/To headers and tags
Route headers
CSeq values
Other SIP state information
4. Create SIP Channels on Another Asterisk
A healthy Asterisk instance is selected and new SIP channels are created with original session information.
5. Set Recovery Channel Variables
Channel variables are set to ensure the new INVITE appears as continuation:
PJSIP_RECOVERY_FROM_DISPLAY
PJSIP_RECOVERY_FROM_URI
PJSIP_RECOVERY_FROM_TAG
PJSIP_RECOVERY_TO_DISPLAY
PJSIP_RECOVERY_TO_URI
PJSIP_RECOVERY_TO_TAG
Call-ID, CSeq, Routes (preserved from original session)
6. Send Recovery INVITE
The INVITE reuses the original Call-ID and tags, so the client interprets it as a re-INVITE within the existing session.
7. Restore RTP and SIP Sessions
Signaling and media are fully re-established, restoring the call to its previous state.
8. Resume Flow Execution
The recovered session resumes Flow execution from before the crash:
Active Calls: Conversation continues without interruption
Conferences: User reconnected to same conference bridge
Call State: All call variables and state restored
Asterisk Patch for Recovery
VoIPBIN patches Asterisk’s PJSIP stack to override SIP header fields based on channel variables:
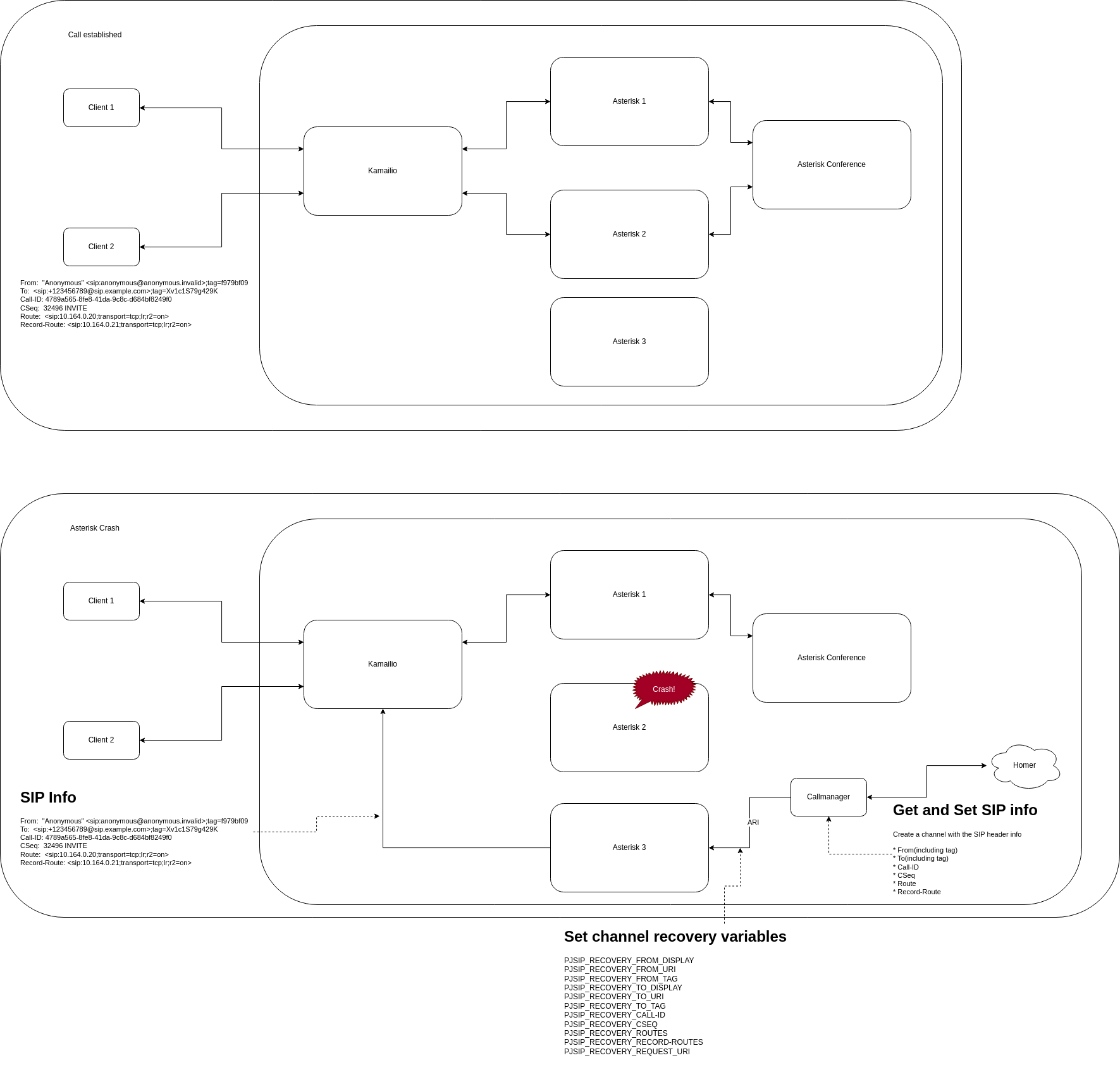
Patch Implementation:
This patch allows a newly created SIP channel to impersonate the original one, making the recovery INVITE appear as a legitimate continuation:
// Extract recovery variables from channel
val_from_display_c_str = pbx_builtin_getvar_helper(session->channel, "PJSIP_RECOVERY_FROM_DISPLAY");
val_from_uri_c_str = pbx_builtin_getvar_helper(session->channel, "PJSIP_RECOVERY_FROM_URI");
val_from_tag_c_str = pbx_builtin_getvar_helper(session->channel, "PJSIP_RECOVERY_FROM_TAG");
val_to_display_c_str = pbx_builtin_getvar_helper(session->channel, "PJSIP_RECOVERY_TO_DISPLAY");
val_to_uri_c_str = pbx_builtin_getvar_helper(session->channel, "PJSIP_RECOVERY_TO_URI");
val_to_tag_c_str = pbx_builtin_getvar_helper(session->channel, "PJSIP_RECOVERY_TO_TAG");
// Call-ID, CSeq, Routes, and other headers are handled similarly
// Override PJSIP headers with recovery values
Full Patch:
The complete implementation is available on GitHub:
Recovery Guarantees:
Transparent to Client: Client sees normal re-INVITE, no indication of crash
State Preservation: All call state and variables restored
Media Continuity: Audio/video streams resume without gaps
Flow Continuity: Call flow resumes at exact point before crash
System Request Flows
Note
AI Context
This page demonstrates detailed request flows through VoIPBIN: creating a call, reading with cache, event broadcasting, multi-service orchestration, real-time WebSocket notifications, and error handling with retries. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand the step-by-step processing of API requests, timing breakdowns, caching behavior, or debugging strategies.
This section demonstrates how requests flow through VoIPBIN’s architecture from client to backend services and back. Understanding these flows helps developers build integrations and debug issues.
Request Flow Overview
All external requests follow this general pattern:
Complete Request Flow:
Client App API Gateway Message Queue Backend Service Data Layer
| | | | |
| HTTP Request | | | |
+------------------>| | | |
| | 1. Authenticate | | |
| | 2. Authorize | | |
| | 3. Validate | | |
| | | | |
| | RPC Request | | |
| +------------------->| | |
| | | Dequeue | |
| | +-------------------->| |
| | | | Query |
| | | +----------------->|
| | | | |
| | | | Result |
| | | |<-----------------+
| | | Response | |
| | |<--------------------+ |
| | RPC Response | | |
| |<-------------------+ | |
| JSON Response | | | |
|<------------------+ | | |
| | | | |
Flow 1: Create Call (Simple)
This flow shows how a basic call creation request flows through the system.
Step-by-Step Flow:
1. Client Request:
Client Application
|
| POST /v1.0/calls
| Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGc...
| Content-Type: application/json
|
| {
| "source": {"type": "tel", "target": "+15551234567"},
| "destinations": [{"type": "tel", "target": "+15559876543"}]
| }
|
v
2. API Gateway (bin-api-manager):
+-------------------------------------------------+
| a) Extract JWT token |
| → token = "eyJhbGc..." |
| |
| b) Validate JWT signature |
| → customer_id = "customer-123" |
| → agent_id = "agent-456" |
| |
| c) Check permissions |
| → hasPermission(customer-123, "call.create")|
| → ✓ Allowed |
| |
| d) Validate request body |
| → Source phone valid |
| → Destination phone valid |
| → ✓ Valid |
| |
| e) Build RPC message |
| { |
| "route": "POST /v1/calls", |
| "headers": { |
| "customer_id": "customer-123", |
| "agent_id": "agent-456" |
| }, |
| "body": {...} |
| } |
| |
| f) Send to RabbitMQ |
| → Queue: bin-manager.call.request |
+-------------------------------------------------+
|
v
3. RabbitMQ:
+------------------------------------------------+
| a) Receive message |
| → Queue: bin-manager.call.request |
| |
| b) Route to available consumer |
| → bin-call-manager instance 2 (of 3) |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
v
4. Call Manager (bin-call-manager):
+-------------------------------------------------+
| a) Receive RPC message |
| → Parse route: POST /v1/calls |
| → Extract customer_id, agent_id |
| |
| b) Validate business logic |
| → Check billing balance |
| → ✓ Sufficient funds |
| |
| c) Create call record |
| → Generate call_id = "call-789" |
| → INSERT INTO calls (...) |
| → Status: "initiating" |
| |
| d) Initiate SIP call |
| → Send to bin-rtc-manager |
| → Request Asterisk channel creation |
| |
| e) Update call status |
| → UPDATE calls SET status='ringing' WHERE...|
| |
| f) Publish event |
| → Event: call.created |
| → RabbitMQ exchange: call.events |
| |
| g) Build response |
| { |
| "id": "call-789", |
| "status": "ringing", |
| "source": "+15551234567", |
| "destination": "+15559876543", |
| "tm_create": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z" |
| } |
| |
| h) Send RPC response |
| → Reply to: reply_to queue |
+-------------------------------------------------+
|
v
5. RabbitMQ (Response):
+------------------------------------------------+
| a) Deliver response to API Gateway |
| → Queue: amq.gen-xyz (reply_to) |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
v
6. API Gateway (Response):
+------------------------------------------------+
| a) Receive RPC response |
| → status_code: 200 |
| → body: {...} |
| |
| b) Format HTTP response |
| → HTTP 201 Created |
| → Content-Type: application/json |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
v
7. Client Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json
{
"id": "call-789",
"status": "ringing",
"source": "+15551234567",
"destination": "+15559876543",
"tm_create": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z"
}
Timing Breakdown:
Component Time Cumulative
---------------------------------------------
API Gateway auth 5ms 5ms
RabbitMQ routing 2ms 7ms
Call Manager logic 30ms 37ms
Database insert 8ms 45ms
RTC Manager SIP setup 50ms 95ms
Response routing 5ms 100ms
---------------------------------------------
Total 100ms
Flow 2: Get Call with Caching
This flow demonstrates cache-aside pattern for reading data.
1. Client Request:
GET /v1.0/calls/call-789
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGc...
|
v
2. API Gateway:
+------------------------------------------------+
| • Authenticate (5ms) |
| • Build RPC message |
| • Send to bin-manager.call.request |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
v
3. Call Manager:
+------------------------------------------------+
| a) Check Redis cache first |
| key = "call:call-789" |
| |
| GET call:call-789 |
| → Cache HIT! (90% of requests) |
| → Return cached data (2ms) |
| |
| OR |
| |
| → Cache MISS (10% of requests) |
| |
| b) If cache miss, query MySQL |
| SELECT * FROM calls WHERE id='call-789' |
| → Query time: 10ms |
| |
| c) Store in Redis for next time |
| SET call:call-789 {...} EX 300 # 5 min |
| → Store time: 2ms |
| |
| d) Check authorization |
| if call.customer_id != jwt.customer_id: |
| return 404 (not 403, for security) |
| |
| e) Return response |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
v
4. Response Times:
Cache Hit Path: ~12ms total
• API Gateway: 5ms
• Redis lookup: 2ms
• Response: 5ms
Cache Miss Path: ~27ms total
• API Gateway: 5ms
• Redis lookup: 2ms (miss)
• MySQL query: 10ms
• Redis store: 2ms
• Response: 5ms
• Authorization: 3ms
Flow 3: Call with Event Broadcasting
This flow shows asynchronous event publishing to multiple subscribers.
Call State Change Flow:
1. Call Answered (in bin-call-manager):
+------------------------------------------------+
| a) Receive SIP 200 OK from Asterisk |
| → Call answered |
| |
| b) Update database |
| UPDATE calls |
| SET status='active', tm_answer=NOW() |
| WHERE id='call-789' |
| |
| c) Invalidate cache |
| DEL call:call-789 |
| |
| d) Publish event to RabbitMQ |
| Exchange: call.events |
| Event: call.answered |
| { |
| "event_type": "call.answered", |
| "call_id": "call-789", |
| "timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:05.000Z" |
| } |
| |
| e) Publish to ZeroMQ (fast path) |
| Topic: "call.state" |
| { |
| "call_id": "call-789", |
| "status": "active" |
| } |
+------------------------------------------------+
|
|
+----------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| | | |
v v v v
2a. Billing Manager 2b. Webhook Manager 2c. Talk Manager 2d. Agent Manager
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+
| Start billing | | Send webhook | | Update agent | | Update agent |
| for call | | to customer | | dashboard | | stats |
| | | endpoint | | via WebSocket | | |
| • Calculate | | | | | | • Active calls |
| charges | | POST https:// | | { | | • Talk time |
| • Create | | customer.com/ | | "event": | | • Status |
| billing | | webhook | | "call. | | |
| record | | | | answered", | | |
| | | { | | "call_id": | | |
| INSERT INTO | | "event_type":| | "call-789" | | |
| billings | | "call. | | } | | |
| (...) | | answered", | | | | |
| | | ... | | | | |
| | | } | | | | |
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+
All subscribers process event independently and concurrently
Flow 4: Complex Multi-Service Flow
This flow demonstrates a complex operation involving multiple services.
Conference Join with Flow Execution:
Client API Gateway Flow Manager Conference Mgr Call Manager
| | | | |
| POST /conferences/ | | | |
| conf-123/join | | | |
+---------------------->| | | |
| | Auth + RPC | | |
| +------------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | | 1. Get Conference | |
| | +------------------->| |
| | | | [conf data] |
| | |<-------------------+ |
| | | | |
| | | 2. Get Flow | |
| | | (from conf) | |
| | | | |
| | | 3. Execute Flow | |
| | | Actions: | |
| | | | |
| | | Action 1: Answer | |
| | +-------------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | Action 2: Talk | |
| | | "Welcome to conf" | |
| | +-------------------------------------->|
| | | | |
| | | Action 3: Join | |
| | | Conference | |
| | +------------------->| |
| | | | Add participant |
| | | | to bridge |
| | |<-------------------+ |
| | | | |
| | Response | | |
| |<-------------------+ | |
| Success | | | |
|<----------------------+ | | |
| | | | |
Services Involved:
• API Gateway (authentication, routing)
• Flow Manager (orchestration)
• Conference Manager (conference state)
• Call Manager (call handling)
• RTC Manager (not shown, handles SIP/media)
Total Time: ~200ms
• Gateway: 5ms
• Conference lookup: 10ms
• Flow execution: 150ms (multiple actions)
• Conference join: 30ms
• Response: 5ms
Flow 5: Real-Time Event Notification
This flow shows how real-time events reach clients via WebSocket.
Real-Time Call Status Updates:
1. Client Subscribes:
Client (Browser) API Gateway (WebSocket) Backend Services
| | |
| WebSocket Connect | |
+-------------------------->| |
| wss://api.voipbin.net/ws | |
| ?token=eyJhbGc... | |
| | Validate JWT |
| | → customer_id: 123 |
| | |
| Subscribe | |
| { | |
| "type": "subscribe", | |
| "topics": [ | |
| "customer_id:123: | |
| call:*" | |
| ] | |
| } | |
+-------------------------->| |
| | Register |
| | subscription |
| | |
| ACK | |
|<--------------------------+ |
| | |
2. Event Occurs:
Call Manager RabbitMQ/ZMQ API Gateway (WS) Client
| | | |
| Call status changed | | |
| (answered) | | |
| | | |
| Publish event | | |
+-------------------------->| | |
| { | | |
| "event": "call. | | |
| answered", | | |
| "customer_id": "123", | | |
| "call_id": "call-789" | | |
| } | | |
| | | |
| | Fanout to | |
| | subscribers | |
| +---------------------->| |
| | | Match topic |
| | | filter |
| | | |
| | | Push to client |
| | +----------------->|
| | | |
| | | { |
| | | "event_type": |
| | | "call. |
| | | answered", |
| | | "call_id": |
| | | "call-789", |
| | | "timestamp": |
| | | "..." |
| | | } |
Latency: < 100ms from event to client notification
Flow 6: Error Handling Flow
This flow demonstrates error handling and retry logic.
Failed Request with Retry:
1. Initial Request (Fails):
API Gateway Call Manager Database
| | |
| RPC: Create Call | |
+------------------>| |
| | INSERT INTO |
| | calls (...) |
| +------------------>|
| | X Connection lost
| | |
| | ← Error |
| |<------------------+
| | |
| | Retry (1s delay) |
| | |
2. Automatic Retry (Attempt 2):
| | Reconnect |
| +------------------>|
| | |
| | INSERT INTO |
| | calls (...) |
| +------------------>|
| | ✓ Success
| | |
| | Success |
| |<------------------+
| | |
| Success | |
|<------------------+ |
| | |
3. Permanent Error (No Retry):
API Gateway Call Manager Billing Manager
| | |
| RPC: Create Call | |
+------------------>| |
| | Check balance |
| +------------------>|
| | |
| | Insufficient |
| | balance |
| |<------------------+
| | |
| Error 402 | Don't retry |
| Payment Required | (permanent error)|
|<------------------+ |
| | |
Error Categories:
• Transient → Retry (network, timeout, connection)
• Permanent → Don't retry (invalid data, permissions)
• Business → Return error (insufficient balance)
Performance Optimization
VoIPBIN optimizes flow performance through several techniques:
Parallel Processing
Sequential vs Parallel:
Sequential (Slow): Parallel (Fast):
+----------+ +----------+
| Task A | 50ms | Task A | 50ms
+----+-----+ +----+-----+
| |
v |
+----------+ |
| Task B | 50ms +-------------+
+----+-----+ | |
| v v
v +----------+ +----------+
+----------+ | Task B | | Task C |
| Task C | 50ms | 50ms | | 50ms |
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+
Total: 150ms Total: 50ms (3x faster)
Caching Strategy
Without Cache: With Cache:
Every request → DB First request → DB
Query time: 10ms Query time: 10ms
Cache for 5 minutes
Subsequent requests → Cache
Query time: 2ms
1000 requests = 10s 1000 requests = 2s (5x faster)
Connection Pooling
No Pooling: With Pooling:
Each request: Each request:
• Connect: 20ms • Get from pool: 1ms
• Query: 10ms • Query: 10ms
• Disconnect: 5ms • Return to pool: 1ms
Total: 35ms Total: 12ms (3x faster)
Best Practices for Developers
When Integrating with VoIPBIN:
Always Include Authentication - Include JWT token in Authorization header - Handle 401 responses (refresh token)
Handle Asynchronous Operations - Many operations are asynchronous - Use webhooks or WebSocket for notifications - Poll with reasonable intervals if needed
Implement Retry Logic - Retry on 5xx errors - Use exponential backoff - Don’t retry on 4xx errors
Subscribe to Events - Use WebSocket for real-time updates - Configure webhooks for important events - Handle duplicate events gracefully
Optimize Requests - Use pagination for lists - Request only needed fields - Cache responses when appropriate
Monitor Performance - Track response times - Alert on high error rates - Monitor webhook delivery
Debugging Request Flows
Using Correlation IDs:
Request Tracing:
1. Client sends request with X-Request-ID header:
POST /v1.0/calls
X-Request-ID: req-abc-123
2. API Gateway logs:
[req-abc-123] Authenticated customer-123
[req-abc-123] Sending RPC to call-manager
3. Call Manager logs:
[req-abc-123] Creating call record
[req-abc-123] Call created: call-789
4. Search logs by correlation ID to trace full flow
Common Issues:
Issue: 401 Unauthorized
→ Check JWT token validity
→ Ensure token not expired
→ Verify customer_id matches resource
Issue: 404 Not Found
→ May be authorization failure (returns 404 for security)
→ Check customer_id ownership
→ Verify resource exists
Issue: 500 Internal Server Error
→ Backend service error
→ Check logs with correlation ID
→ May require retry
Issue: Slow Response
→ Check cache hit rate
→ Review database query performance
→ Monitor service health
Summary
VoIPBIN’s request flows are designed for:
Performance: Caching, connection pooling, parallel processing
Reliability: Retry logic, circuit breakers, health checks
Scalability: Stateless services, horizontal scaling, queue-based communication
Observability: Correlation IDs, distributed tracing, comprehensive logging
Security: Gateway authentication, authorization checks, encrypted communication
Understanding these flows helps developers build efficient integrations and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Call Flow Sequences
Note
AI Context
This page provides detailed sequence diagrams for VoIPBIN’s core operations: inbound call flow (PSTN to flow execution), outbound campaign flow, AI voice assistant (Pipecat hybrid architecture), call transfer sequences (blind and attended), queue call distribution, conference join, and webhook delivery. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand the exact component interactions for specific call scenarios or integration points.
This section provides detailed sequence diagrams for VoIPBIN’s core call flows, showing how components interact during real-world scenarios.
Inbound Call Flow
When an external caller dials a VoIPBIN number, the following sequence occurs:
Inbound Call Flow:
PSTN Carrier Kamailio Asterisk asterisk-proxy call-manager flow-manager
| | | | | |
| SIP INVITE | | | | |
+------------>| | | | |
| | Route | | | |
| +----------->| | | |
| | | Channel | | |
| | | Created | | |
| | +------------->| | |
| | | | Publish: | |
| | | | asterisk.all.event |
| | | +--------------->| |
| | | | | |
| | | | | Create Call |
| | | | | Record |
| | | | | |
| | | | | Lookup Number |
| | | | | -> Flow ID |
| | | | | |
| | | | | RPC: Start |
| | | | | ActiveFlow |
| | | | +-------------->|
| | | | | |
| | | | | | Execute
| | | | | | Actions
| | | | | |
| | | | RPC: Answer | |
| | |<-----------------------------------+----------+
| | | | | |
| 200 OK | | | | |
|<------------+------------+ | | |
| | | | | |
| RTP Media Established | | | |
|<------------------------>| | | |
| | | | | |
Key Components:
Kamailio - Receives SIP INVITE, routes to appropriate Asterisk instance
Asterisk - Creates SIP channel, generates ARI events via ARI WebSocket
asterisk-proxy - Bridges ARI events to RabbitMQ (
asterisk.all.eventqueue)call-manager - Processes events, creates call record, initiates flow
flow-manager - Executes the configured call flow (IVR actions)
Event Routing in call-manager:
asterisk-proxy Event Routing:
asterisk.all.event
|
v
+------------------+
| subscribehandler |
+--------+---------+
|
| Routes by event type
v
+------------------+
| arieventhandler |
+--------+---------+
|
+-------+-------+
| |
v v
+----------+ +----------+
|channelhdl| |bridgehdl |
+----------+ +----------+
| |
v v
Channel Bridge
Events Events
(create, (join,
hangup, leave)
dtmf)
Channel Events:
StasisStart- Channel enters Stasis application (call starts)StasisEnd- Channel exits Stasis (call ends)ChannelDtmfReceived- DTMF digit pressedChannelHangupRequest- Hangup initiatedChannelStateChange- Channel state changed (ringing, up, etc.)
Bridge Events:
ChannelEnteredBridge- Participant joined bridge (conference)ChannelLeftBridge- Participant left bridge
Outbound Campaign Flow
Outbound campaigns automate calling lists of targets:
Campaign Execution Flow:
API Request campaign-mgr outdial-mgr call-manager flow-manager
| | | | |
| Start | | | |
| Campaign | | | |
+------------>| | | |
| | | | |
| | Get Targets | | |
| | (Outplan) | | |
| +-------------->| | |
| | | | |
| |<--------------+ | |
| | Dial Targets | | |
| | | | |
| | For each target: | |
| +------------------------------------------+ |
| | | | | |
| | RPC: Create | | | |
| | Outbound Call | | | |
| +------------------------------>| | |
| | | | | |
| | | | Asterisk | |
| | | | Originate| |
| | | +--------->| |
| | | | | |
| | | | Answer? | |
| | | |<---------+ |
| | | | | |
| | | | If answered: |
| | | | Start Flow |
| | | +-------------->|
| | | | |
| | | | | Execute
| | | | | Actions
| | | | | (play,
| | | | | gather,
| | | | | ai_talk)
| | | | |
| | Event: | | |
| | call_hungup | | |
| |<------------------------------+ |
| | | | |
| | Update | | |
| | Campaign | | |
| | Status | | |
| +------------------------------------------+ |
| | |
| | Continue with next target... |
| | |
Campaign Components:
campaign-manager - Orchestrates campaign execution, tracks progress
outdial-manager - Manages dial targets (outplans), provides next numbers to dial
call-manager - Creates and manages individual calls
flow-manager - Executes call flow when target answers
Campaign Events:
Event Subscriptions:
campaign-manager subscribes to:
+--------------------------------+
| o call_hungup | - Track call completion
| o activeflow_deleted | - Track flow completion
| o call_answered | - Track answer rates
+--------------------------------+
Event triggers campaign state updates:
o Calculate dial success rate
o Move to next target
o Update campaign statistics
AI Voice Assistant Flow (Pipecat)
VoIPBIN’s AI voice assistant uses a hybrid Go+Python architecture:
Pipecat AI Voice Architecture:
Asterisk pipecat-manager (Go) pipecat-runner (Python) LLM
| | | |
| | | |
| Audiosocket | | |
| (8kHz ulaw) | | |
+------------------>| | |
| | | |
| | WebSocket | |
| | (16kHz PCM) | |
| +------------------------->| |
| | | |
| | | STT: Deepgram |
| | | "What's the weather?"|
| | +-------------------->|
| | | |
| | |<--------------------+
| | | LLM Response |
| | | |
| | | TTS: Generate Audio |
| | | |
| |<-------------------------+ |
| | Audio Response | |
| | | |
|<------------------+ | |
| Play to Caller | | |
| | | |
Audio Processing Pipeline:
Audio Resampling:
Asterisk pipecat-manager pipecat-runner
(8kHz ulaw) (Go Resampler) (16kHz PCM)
| | |
| Audiosocket | |
| (8kHz ulaw) | |
+---------------------->| |
| | |
| | Resample |
| | 8kHz -> 16kHz |
| | ulaw -> PCM |
| | |
| | WebSocket |
| | (Protobuf frame) |
| +---------------------------->|
| | |
| | WebSocket |
| | (Protobuf response) |
| |<----------------------------+
| | |
| | Resample |
| | 16kHz -> 8kHz |
| | PCM -> ulaw |
| | |
|<----------------------+ |
| Audiosocket | |
| (8kHz ulaw) | |
| | |
Why Hybrid Architecture:
Go (pipecat-manager): Efficient audio handling, low-latency resampling, integration with VoIPBIN RPC
Python (pipecat-runner): Rich AI/ML ecosystem, Pipecat framework, easy LLM integration
Protobuf Frame Format:
Frame Message:
+----------------------------------+
| type: FrameType |
| o INPUT_AUDIO_RAW (16kHz PCM) |
| o OUTPUT_AUDIO_RAW |
| o CONTROL (start/stop) |
| o LLM_FUNCTION_CALL |
| o LLM_FUNCTION_CALL_RESULT |
+----------------------------------+
| data: bytes (audio samples) |
+----------------------------------+
| timestamp: int64 |
+----------------------------------+
LLM Tool Calling:
Tool Call Flow:
LLM pipecat-runner pipecat-manager External API
| | | |
| "Transfer to sales" | | |
+------------------------->| | |
| | | |
| | Frame: LLM_FUNCTION_CALL |
| | tool: "transfer_call" | |
| | args: {dept: "sales"} | |
| +----------------------->| |
| | | |
| | | RPC: Transfer |
| | | Call |
| | +------------------->|
| | | |
| | |<-------------------+
| | | Success |
| | | |
| | Frame: FUNCTION_CALL_RESULT |
| | result: "transferred" | |
| |<-----------------------+ |
| | | |
|<-------------------------+ | |
| "Transferred to sales" | | |
| | | |
Available AI Tools:
transfer_call- Transfer to another extension/queueend_call- End the conversationsend_sms- Send SMS to callercreate_ticket- Create support ticketlookup_customer- Query CRM for customer infoschedule_callback- Schedule callback appointment
Call Transfer Sequence
Call transfers involve coordination between multiple services:
Blind Transfer Flow:
Agent A call-manager flow-manager Asterisk Agent B
| | | | |
| Transfer | | | |
| Request | | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | | | |
| | Create | | |
| | Transfer | | |
| | Record | | |
| | | | |
| | RPC: Start | | |
| | Transfer Flow| | |
| +------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | | Action: | |
| | | Redirect | |
| | +------------->| |
| | | | |
| | | | REFER |
| | | +------------->|
| | | | |
| | | |<-------------+
| | | | 200 OK |
| | | | |
| | Event: | | |
| Disconnected | transfer_ | | |
|<-------------+ completed | | |
| | | | |
| | | | RTP Media |
| | | Caller <------------------>|
| | | | |
Attended Transfer Flow:
Attended Transfer:
Agent A call-manager Asterisk Agent B Caller
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Consult B | | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | Create | | |
| | Consult Call | | |
| +------------->| | |
| | +----------->| |
| | | | |
|<------- Consult Active ---->| | |
| | | | |
| (Discusses with B) | | |
| | | | |
| Complete | | | |
| Transfer | | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | Bridge | | |
| | B <-> Caller | | |
| +------------->| | |
| | |<----------------------->|
| | | RTP Media |
| | | | |
| Disconnected | | | |
|<-------------+ | | |
| | | | |
Queue Call Distribution
Queue management distributes calls to available agents:
Queue Call Flow:
Caller flow-manager queue-manager agent-manager Agent
| | | | |
| Incoming Call| | | |
+------------->| | | |
| | | | |
| | Action: | | |
| | queue_join | | |
| +------------->| | |
| | | | |
| | | Get Available | |
| | | Agents | |
| | +---------------->| |
| | | | |
| | |<----------------+ |
| | | [agent1, agent2]| |
| | | | |
| | | Ring Strategy | |
| | | (round-robin, | |
| | | longest-idle) | |
| | | | |
| | | Offer Call | |
| | +------------------------------>|
| | | | |
| | |<------------------------------+
| | | Agent Accepts | |
| | | | |
| |<-------------+ | |
| | Exit Queue | | |
| | | | |
| | Action: | | |
| | Connect | | |
| | Agent<->Caller | |
| | | | |
|<------- Media Connected ------------------------>| |
| | | | |
Queue Features:
Ring Strategies: round-robin, longest-idle, least-calls, ring-all
Queue Timeout: Max wait time before alternative action
Queue Music: Hold music or announcements while waiting
Position Announcements: “You are caller number 3 in queue”
Agent Wrap-up: Post-call processing time before next call
Conference Join Sequence
Multi-party conferences use dedicated infrastructure:
Conference Join Flow:
Participant flow-manager conf-manager Asterisk-Conf
| | | |
| Call Arrives | | |
+------------->| | |
| | | |
| | Action: | |
| | conference_join |
| +-------------->| |
| | | |
| | | Get/Create |
| | | Conference |
| | +--------------->|
| | | |
| | | ARI: Create |
| | | Bridge |
| | |<---------------+
| | | bridge_id |
| | | |
| | | ARI: Add |
| | | Channel to |
| | | Bridge |
| | +--------------->|
| | | |
| |<--------------+ |
| | Participant | |
| | Joined | |
| | | |
| Audio Mixed | | |
|<-------------------------------------------->|
| | | |
| | Event: | |
| | confbridge_ | |
| | joined | |
| +-------------->| |
| | | |
Conference Events Published:
Conference Events:
confbridge_joined
+----------------------------------+
| conference_id: uuid |
| participant_id: uuid |
| call_id: uuid |
| participant_count: int |
+----------------------------------+
confbridge_left
+----------------------------------+
| conference_id: uuid |
| participant_id: uuid |
| reason: "hangup" | "kick" |
| participant_count: int |
+----------------------------------+
confbridge_record_started
+----------------------------------+
| conference_id: uuid |
| recording_id: uuid |
+----------------------------------+
Webhook Delivery Flow
Events trigger webhook notifications to customer endpoints:
Webhook Delivery:
call-manager RabbitMQ webhook-manager Customer Endpoint
| | | |
| Event: | | |
| call_hungup | | |
+------------->| | |
| | | |
| | Fanout to | |
| | Subscribers | |
| +-------------->| |
| | | |
| | | Lookup Webhook |
| | | Config for |
| | | Customer |
| | | |
| | | POST Event |
| | +------------------>|
| | | |
| | | Retry on Failure |
| | | (exponential |
| | | backoff) |
| | | |
| | |<------------------+
| | | 200 OK |
| | | |
| | | Mark Delivered |
| | | |
Webhook Retry Policy:
Retry Strategy:
+----------------------------------+
| Attempt 1: Immediate |
| Attempt 2: 1 minute delay |
| Attempt 3: 5 minutes delay |
| Attempt 4: 30 minutes delay |
| Attempt 5: 2 hours delay |
+----------------------------------+
| Max Attempts: 5 |
| Total Window: ~2.5 hours |
+----------------------------------+
Webhook Payload:
POST https://customer.example.com/webhook
Content-Type: application/json
X-VoIPBIN-Signature: sha256=...
{
"type": "call_hungup",
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"data": {
"id": "call-123",
"customer_id": "customer-456",
"source": "+15551234567",
"destination": "+15559876543",
"duration": 120,
"status": "completed",
"hangup_cause": "normal_clearing"
}
}
Deployment Architecture
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s production deployment on Google Cloud Platform: GKE cluster configuration, Kubernetes deployment patterns, HPA auto-scaling, VoIP VM infrastructure (Kamailio, Asterisk, RTPEngine), database and cache infrastructure, network architecture (VPC, firewall rules), CI/CD pipeline (CircleCI), and disaster recovery. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand infrastructure sizing, scaling limits, deployment strategies, or network topology.
VoIPBIN runs on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) using Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for container orchestration. This section details the deployment topology, scaling strategies, and infrastructure components.
Infrastructure Overview
VoIPBIN Production Infrastructure:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Google Cloud Platform |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| +------------------------+ +------------------------+ |
| | GKE Cluster | | Cloud SQL (MySQL) | |
| | (Kubernetes) | | - Primary | |
| | | | - Read Replicas (3) | |
| | 30+ Microservices | +------------------------+ |
| | 2 replicas each | |
| +------------------------+ +------------------------+ |
| | Memorystore (Redis) | |
| +------------------------+ | - 16 GB Instance | |
| | Compute Engine VMs | +------------------------+ |
| | - Kamailio (3) | |
| | - Asterisk (6+) | +------------------------+ |
| | - RTPEngine (3) | | Cloud Storage | |
| +------------------------+ | - Recordings | |
| | - Media files | |
| +------------------------+ +------------------------+ |
| | RabbitMQ Cluster | |
| | (3-node) | +------------------------+ |
| +------------------------+ | Cloud Load Balancer | |
| +------------------------+ |
| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Kubernetes Architecture
All Go microservices run in Kubernetes:
GKE Cluster Configuration:
+----------------------------------------------------------------+
| GKE Cluster |
+----------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Namespace: production |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | Deployment: bin-api-manager (2 replicas) | |
| | +----------------+ +----------------+ | |
| | | Pod 1 | | Pod 2 | | |
| | | - api-manager | | - api-manager | | |
| | | - Port: 443 | | - Port: 443 | | |
| | | - Port: 9000 | | - Port: 9000 | | |
| | | - Port: 2112 | | - Port: 2112 | | |
| | +----------------+ +----------------+ | |
| | | |
| | Deployment: bin-call-manager (2 replicas) | |
| | +----------------+ +----------------+ | |
| | | Pod 1 | | Pod 2 | | |
| | +----------------+ +----------------+ | |
| | | |
| | ... (28 more deployments, each with 2 replicas) | |
| | | |
| +-----------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+----------------------------------------------------------------+
Standard Deployment Pattern:
All services follow the same deployment pattern:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: bin-call-manager
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: bin-call-manager
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: bin-call-manager
image: gcr.io/voipbin/bin-call-manager:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080 # Health check
- containerPort: 2112 # Prometheus metrics
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "100m"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /ready
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
env:
- name: DSN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: db-credentials
key: dsn
- name: RABBIT_ADDR
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: app-config
key: rabbit_addr
Pod Ports:
Service Port Configuration:
bin-api-manager:
+------------------------------------------+
| Port 443 - HTTPS REST API (external) |
| Port 9000 - Audiosocket (media stream) |
| Port 2112 - Prometheus metrics |
+------------------------------------------+
Other Services:
+------------------------------------------+
| Port 8080 - Health/Ready endpoints |
| Port 2112 - Prometheus metrics |
+------------------------------------------+
Service Scaling
VoIPBIN scales services based on demand:
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA):
HPA Configuration:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: bin-call-manager-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: bin-call-manager
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 80
Scaling Triggers:
Auto-Scaling Strategy:
+---------------------------------------------+
| Metric | Threshold | Action |
+---------------------------------------------+
| CPU > 70% | Scale up | +1 replica |
| CPU < 30% | Scale down| -1 replica |
| Memory > 80% | Scale up | +1 replica |
| Queue depth >100| Scale up | +2 replicas |
+---------------------------------------------+
Scaling Limits:
+---------------------------------------------+
| Service | Min | Max | Notes |
+---------------------------------------------+
| bin-api-manager | 2 | 20 | Gateway |
| bin-call-manager | 2 | 10 | Core |
| bin-flow-manager | 2 | 10 | Core |
| bin-ai-manager | 2 | 5 | GPU |
| bin-pipecat-manager | 2 | 8 | AI |
| Other services | 2 | 5 | Standard|
+---------------------------------------------+
VoIP Infrastructure
VoIP components run on dedicated VMs for performance:
VoIP Component Topology:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| External Traffic |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
| SIP (UDP/TCP 5060-5061)
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Cloud Load Balancer |
| (L4 - TCP/UDP) |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| | |
v v v
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+
| Kamailio-1 | | Kamailio-2 | | Kamailio-3 |
| (SIP Proxy) | | (SIP Proxy) | | (SIP Proxy) |
| | | | | |
| n1-standard-4 | | n1-standard-4 | | n1-standard-4 |
| 4 vCPU, 15GB | | 4 vCPU, 15GB | | 4 vCPU, 15GB |
+-------+--------+ +-------+--------+ +-------+--------+
| | |
+-------------------+-------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Internal Load Balancer |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| | |
v v v
+----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+
| Asterisk-1 | | Asterisk-2 | | Asterisk-3 |
| (Call Farm) | | (Call Farm) | | (Conf Farm) |
| | | | | |
| n1-standard-8 | | n1-standard-8 | | n1-standard-8 |
| 8 vCPU, 30GB | | 8 vCPU, 30GB | | 8 vCPU, 30GB |
+-------+--------+ +-------+--------+ +-------+--------+
| | |
+-------------------+-------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| RTPEngine Farm |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| +----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+ |
| | RTPEngine-1 | | RTPEngine-2 | | RTPEngine-3 | |
| | n1-highcpu-8 | | n1-highcpu-8 | | n1-highcpu-8 | |
| +----------------+ +----------------+ +----------------+ |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
VM Specifications:
VoIP VM Sizing:
Kamailio Nodes (SIP Proxy):
+-------------------------------------------+
| Machine Type: n1-standard-4 |
| vCPUs: 4 |
| Memory: 15 GB |
| Disk: 100 GB SSD |
| Network: 10 Gbps |
| Capacity: ~5,000 concurrent calls |
+-------------------------------------------+
Asterisk Nodes (Media Server):
+-------------------------------------------+
| Machine Type: n1-standard-8 |
| vCPUs: 8 |
| Memory: 30 GB |
| Disk: 200 GB SSD |
| Network: 10 Gbps |
| Capacity: ~500 concurrent calls each |
+-------------------------------------------+
RTPEngine Nodes (Media Proxy):
+-------------------------------------------+
| Machine Type: n1-highcpu-8 |
| vCPUs: 8 |
| Memory: 7.2 GB |
| Disk: 50 GB SSD |
| Network: 10 Gbps |
| Capacity: ~2,000 media streams each |
+-------------------------------------------+
Database Infrastructure
Cloud SQL for MySQL provides managed database:
Cloud SQL Configuration:
Primary Instance:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Instance: db-custom-8-32768 |
| vCPUs: 8 |
| Memory: 32 GB |
| Storage: 1 TB SSD |
| High Avail: Regional (failover) |
| Backups: Daily automatic |
+-------------------------------------------+
Read Replicas (3):
+-------------------------------------------+
| Instance: db-custom-4-16384 |
| vCPUs: 4 |
| Memory: 16 GB |
| Storage: 1 TB SSD |
| Region: Same as primary |
+-------------------------------------------+
Replication Architecture:
+-------------------------------------------+
| |
| +-----------+ |
| | Primary |<-- All Writes |
| +-----------+ |
| | |
| | Async Replication |
| | |
| +----+----+----+ |
| | | | | |
| v v v v |
| R1 R2 R3 (Backups) |
| ^ ^ ^ |
| | | | |
| +----+----+ |
| | |
| +--- Read Traffic |
| |
+-------------------------------------------+
Cache Infrastructure
Memorystore for Redis provides caching:
Memorystore Configuration:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Tier: Standard |
| Capacity: 16 GB |
| Version: Redis 6.x |
| High Avail: Yes (failover replica) |
| Max Conn: 65,000 |
| Network: Private VPC |
+-------------------------------------------+
Cache Distribution:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Data Type | Approx Size | TTL |
+-------------------------------------------+
| Session tokens | 2 GB | 1 hour |
| Call records | 4 GB | 24 hours|
| Agent status | 1 GB | 5 min |
| Configuration | 500 MB | 1 hour |
| Queue stats | 500 MB | 1 min |
| Flow definitions | 2 GB | 1 hour |
| Other | 6 GB | varies |
+-------------------------------------------+
Message Queue Infrastructure
RabbitMQ cluster for messaging:
RabbitMQ Cluster:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Node 1 (Primary) |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Queues: 50% of messages | |
| | CPU: 4 vCPU | |
| | Memory: 16 GB | |
| | Disk: 100 GB SSD | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| |
| Node 2 (Mirror) |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Queues: Mirrored from Node 1 | |
| | CPU: 4 vCPU | |
| | Memory: 16 GB | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| |
| Node 3 (Mirror) |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Queues: Mirrored from Node 1 | |
| | CPU: 4 vCPU | |
| | Memory: 16 GB | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------------------+
Queue Mirroring Policy:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Pattern: bin-manager.* |
| ha-mode: all |
| ha-sync-mode: automatic |
+-------------------------------------------+
Network Architecture
VPC network isolates components:
VPC Network Design:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| VPC: voipbin-prod |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| Subnet: public (10.0.0.0/24) |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Cloud Load Balancer | |
| | NAT Gateway | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| Subnet: kubernetes (10.0.1.0/24) |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | GKE Cluster (all pods) | |
| | Internal Load Balancers | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| Subnet: voip (10.0.2.0/24) |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Kamailio VMs | |
| | Asterisk VMs | |
| | RTPEngine VMs | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
| Subnet: data (10.0.3.0/24) |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Cloud SQL (private IP) | |
| | Memorystore (private IP) | |
| | RabbitMQ Cluster | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Firewall Rules:
Firewall Configuration:
Ingress (External):
+-------------------------------------------+
| Rule | Ports | Source |
+-------------------------------------------+
| allow-https | 443 | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| allow-sip | 5060-5061| 0.0.0.0/0 |
| allow-rtp | 10000-60000| 0.0.0.0/0|
+-------------------------------------------+
Internal:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Rule | Ports | Source |
+-------------------------------------------+
| allow-k8s-internal| all | 10.0.1.0/24|
| allow-voip-internal| all | 10.0.2.0/24|
| allow-db-access | 3306,6379| 10.0.1.0/24|
| allow-rabbit | 5672 | 10.0.1.0/24|
+-------------------------------------------+
Load Balancing
Multiple load balancers route traffic:
Load Balancer Architecture:
External (L7 - HTTPS):
+-------------------------------------------+
| api.voipbin.net |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Cloud Load Balancer (HTTPS) | |
| | - SSL termination | |
| | - Path routing | |
| | - Health checks | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | |
| v |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | GKE Ingress -> api-manager | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------------------+
External (L4 - SIP):
+-------------------------------------------+
| sip.voipbin.net |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Network Load Balancer (TCP/UDP)| |
| | - Port 5060 (UDP/TCP) | |
| | - Port 5061 (TLS) | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | |
| v |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Kamailio Farm | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------------------+
Internal (Services):
+-------------------------------------------+
| Kubernetes Service (ClusterIP) |
| - bin-call-manager:8080 |
| - bin-flow-manager:8080 |
| - ... |
+-------------------------------------------+
Monitoring Stack
Prometheus and Grafana for observability:
Monitoring Architecture:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Grafana Dashboard |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Service Health | |
| | Call Metrics | |
| | Queue Depths | |
| | Error Rates | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------------------+
^
|
+-------------------------------------------+
| Prometheus |
| +----------------------------------+ |
| | Scrape interval: 15s | |
| | Retention: 30 days | |
| | Storage: 100 GB | |
| +----------------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------------------+
^
|
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
| | | | | |
v v v v v v
api call flow ai voip db
:2112 :2112 :2112 :2112 :9100 :9104
Key Metrics Collected:
Prometheus Metrics:
Service Metrics (port 2112):
+-------------------------------------------+
| voipbin_http_requests_total |
| voipbin_http_request_duration_seconds |
| voipbin_rpc_requests_total |
| voipbin_rpc_request_duration_seconds |
| voipbin_active_calls_gauge |
| voipbin_queue_depth_gauge |
+-------------------------------------------+
Infrastructure Metrics:
+-------------------------------------------+
| container_cpu_usage_seconds_total |
| container_memory_usage_bytes |
| mysql_global_status_threads_connected |
| redis_connected_clients |
| rabbitmq_queue_messages |
+-------------------------------------------+
Deployment Pipeline
CI/CD with CircleCI:
Deployment Pipeline:
Developer GitHub CircleCI GKE
| | | |
| Push | | |
+-------------->| | |
| | Webhook | |
| +------------->| |
| | | |
| | | 1. Checkout |
| | | 2. Test |
| | | 3. Lint |
| | | 4. Build |
| | | 5. Push Image|
| | | |
| | | (if main) |
| | | 6. Deploy |
| | +------------->|
| | | |
| | | | Rolling
| | | | Update
| | | |
| | |<-------------+
| | | Deploy Done |
| | | |
Rolling Update Strategy:
Deployment Strategy:
spec:
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1 # Create 1 new pod at a time
maxUnavailable: 0 # Never have 0 ready pods
Update Flow:
+-------------------------------------------+
| 1. New pod created with new version |
| 2. Wait for readiness probe success |
| 3. Remove old pod from service |
| 4. Terminate old pod |
| 5. Repeat for all replicas |
+-------------------------------------------+
Zero-Downtime:
- At least 1 pod always ready
- No traffic to terminating pods
- Graceful shutdown (SIGTERM)
Disaster Recovery
Multi-region resilience:
DR Strategy:
Primary Region: us-central1
+-------------------------------------------+
| GKE Cluster (Active) |
| Cloud SQL Primary |
| Memorystore |
| VoIP VMs |
+-------------------------------------------+
DR Region: us-east1 (Standby)
+-------------------------------------------+
| GKE Cluster (Warm Standby) |
| Cloud SQL Replica |
| Memorystore (Separate) |
| VoIP VMs (Ready to scale) |
+-------------------------------------------+
Recovery Objectives:
+-------------------------------------------+
| RTO (Recovery Time): < 30 minutes |
| RPO (Data Loss): < 5 minutes |
+-------------------------------------------+
Failover Procedure:
DR Failover Steps:
1. Detect Failure
+----------------------------------+
| - Monitor alerts trigger |
| - Confirm region outage |
+----------------------------------+
2. Database Failover
+----------------------------------+
| - Promote DR replica to primary |
| - Update connection strings |
+----------------------------------+
3. Traffic Redirect
+----------------------------------+
| - Update DNS (Cloud DNS) |
| - Route traffic to DR region |
+----------------------------------+
4. Scale DR Resources
+----------------------------------+
| - Scale GKE deployments |
| - Start additional VoIP VMs |
+----------------------------------+
5. Verify Services
+----------------------------------+
| - Health checks pass |
| - Test critical paths |
+----------------------------------+
Cost Optimization
Resource efficiency strategies:
Cost Optimization:
Committed Use Discounts:
+-------------------------------------------+
| GKE nodes: 3-year commitment (57%) |
| Cloud SQL: 3-year commitment (57%) |
| Memorystore: 1-year commitment (25%) |
+-------------------------------------------+
Preemptible VMs (non-critical):
+-------------------------------------------+
| CI/CD runners: Preemptible (80% savings) |
| Batch jobs: Preemptible |
+-------------------------------------------+
Right-sizing:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Monthly review of resource utilization |
| Downsize underutilized instances |
| Upsize bottlenecked services |
+-------------------------------------------+
Auto-scaling:
+-------------------------------------------+
| Scale down during off-peak hours |
| Scale up only when needed |
| Set appropriate min/max replicas |
+-------------------------------------------+
Security Architecture
Note
AI Context
This page describes VoIPBIN’s security architecture: four defense-in-depth layers (edge, API gateway, internal services, data), JWT and Access Key authentication, RBAC authorization model, transport security (TLS, SRTP), Kubernetes secrets management, network isolation (VPC, firewall rules, network policies), input validation, rate limiting, DDoS protection, audit logging, data protection, and compliance frameworks. Relevant when an AI agent needs to understand authentication flows, permission models, or security controls.
VoIPBIN implements defense-in-depth security across all layers, from API authentication to data encryption. This section details the security architecture, authentication flows, and protection mechanisms.
Security Overview
Security Layers:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| External Clients |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Layer 1: Edge Security |
| o TLS 1.3 encryption |
| o DDoS protection (Cloud Armor) |
| o WAF rules |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Layer 2: API Gateway (bin-api-manager) |
| o JWT/AccessKey authentication |
| o Authorization checks |
| o Rate limiting |
| o Input validation |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Layer 3: Internal Services |
| o Network isolation (VPC) |
| o Service-to-service trust |
| o No external exposure |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Layer 4: Data Layer |
| o Encryption at rest |
| o Encrypted connections |
| o Access controls |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Authentication Architecture
VoIPBIN supports two authentication methods: JWT tokens and Access Keys.
Authentication Flow:
JWT Authentication Flow:
Client API Gateway Auth Service
| | |
| POST /auth/login | |
| (username, password) | |
+----------------------->| |
| | |
| | Validate Credentials |
| +------------------------>|
| | |
| |<------------------------+
| | User Valid + Permissions|
| | |
| | Generate JWT Token |
| | (HS256 signed) |
| | |
|<-----------------------+ |
| { "token": "eyJ..." } | |
| | |
| | |
| GET /v1/calls | |
| Authorization: Bearer eyJ... |
+----------------------->| |
| | |
| | Validate JWT: |
| | 1. Verify signature |
| | 2. Check expiration |
| | 3. Extract claims |
| | |
| | Route to call-manager |
| | (with customer_id) |
| | |
|<-----------------------+ |
| { calls: [...] } | |
| | |
JWT Token Structure:
JWT Token Claims:
Header:
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
Payload:
{
"customer_id": "uuid", // Customer UUID
"agent_id": "uuid", // Agent UUID (optional)
"permissions": [ // Permission list
"customer_admin",
"call_create",
"call_read"
],
"iat": 1706000000, // Issued at
"exp": 1706003600 // Expires (1 hour)
}
Signature:
HMACSHA256(
base64UrlEncode(header) + "." +
base64UrlEncode(payload),
secret
)
Access Key Authentication:
Access Key Flow:
Client API Gateway
| |
| GET /v1/calls |
| Authorization: AccessKey ak_xxxxx
+----------------------->|
| |
| | Lookup Access Key:
| | 1. Find in database
| | 2. Verify not expired
| | 3. Check permissions
| | 4. Get customer_id
| |
| | Route to call-manager
| | (with customer_id)
| |
|<-----------------------+
| { calls: [...] } |
| |
Access Key Structure:
Access Key:
+------------------------------------------+
| Format: ak_<32-character-random-string> |
| Example: ak_a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0k1l2m3n4|
+------------------------------------------+
Database Record:
+------------------------------------------+
| id: UUID |
| customer_id: UUID |
| key_hash: SHA256 hash of key |
| permissions: JSON array |
| tm_expire: Expiration timestamp |
| tm_create: Creation timestamp |
+------------------------------------------+
Transport Security
All communication encrypted:
External TLS:
TLS Configuration:
api.voipbin.net:
+------------------------------------------+
| Protocol: TLS 1.3 (minimum TLS 1.2) |
| Cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384|
| Certificate: Let's Encrypt (auto-renew)|
| HSTS: Enabled (max-age=31536000) |
+------------------------------------------+
SIP TLS (sip.voipbin.net:5061):
+------------------------------------------+
| Protocol: TLS 1.2+ |
| Certificate: Let's Encrypt |
| Client Auth: Optional |
+------------------------------------------+
Internal Encryption:
Internal Communications:
Kubernetes Pod-to-Pod:
+------------------------------------------+
| Network Policies enforce isolation |
| Internal traffic within VPC only |
| No TLS required (trusted network) |
+------------------------------------------+
Database Connections:
+------------------------------------------+
| Cloud SQL: SSL required |
| Redis: In-transit encryption |
| RabbitMQ: TLS between nodes |
+------------------------------------------+
SRTP for Media:
Media Encryption:
WebRTC Calls:
+------------------------------------------+
| Protocol: SRTP (DTLS-SRTP) |
| Key Exchange: DTLS 1.2 |
| Cipher: AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80 |
+------------------------------------------+
SIP TLS Calls:
+------------------------------------------+
| Signaling: SIP over TLS |
| Media: SRTP (negotiated via SDP) |
+------------------------------------------+
PSTN Calls:
+------------------------------------------+
| Internal: SRTP within VoIPBIN |
| To Carrier: Depends on carrier support |
+------------------------------------------+
Secrets Management
Kubernetes secrets store sensitive data:
Secret Types:
Kubernetes Secrets:
Database Credentials:
+------------------------------------------+
| Secret: db-credentials |
| Keys: |
| - dsn: mysql://user:pass@host/db |
| - username: voipbin_app |
| - password: <encrypted> |
+------------------------------------------+
JWT Signing Key:
+------------------------------------------+
| Secret: jwt-secret |
| Keys: |
| - key: <256-bit random key> |
+------------------------------------------+
API Keys (External Services):
+------------------------------------------+
| Secret: external-api-keys |
| Keys: |
| - deepgram_api_key |
| - openai_api_key |
| - twilio_api_key |
+------------------------------------------+
SSL Certificates:
+------------------------------------------+
| Secret: ssl-certs |
| Keys: |
| - tls.crt: <certificate> |
| - tls.key: <private key> |
+------------------------------------------+
Secret Injection:
Pod Secret Configuration:
spec:
containers:
- name: bin-api-manager
env:
- name: DSN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: db-credentials
key: dsn
- name: JWT_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: jwt-secret
key: key
volumeMounts:
- name: ssl-certs
mountPath: /etc/ssl/voipbin
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: ssl-certs
secret:
secretName: ssl-certs
Base64 Encoding:
CLI Flag Pattern:
Some services accept base64-encoded secrets via CLI:
+------------------------------------------+
| -ssl_cert_base64=<base64-encoded-cert> |
| -ssl_private_base64=<base64-encoded-key> |
+------------------------------------------+
Why Base64:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Allows passing binary data via env vars|
| o Avoids special character issues |
| o Decoded at runtime in application |
+------------------------------------------+
Network Security
VPC and firewall protection:
Network Isolation:
Network Segmentation:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| VPC: voipbin-prod |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
| DMZ (Public Subnet): |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Cloud Load Balancer (External IP) | |
| | - Only port 443 (HTTPS) | |
| | - Only port 5060/5061 (SIP) | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | |
| | Internal Only |
| v |
| Application Subnet: |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | GKE Pods (No external IPs) | |
| | VoIP VMs (Internal IPs) | |
| | - Outbound via NAT Gateway only | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | |
| v |
| Data Subnet: |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| | Cloud SQL (Private IP only) | |
| | Memorystore (Private IP only) | |
| | RabbitMQ (Private IP only) | |
| +-------------------------------------------------------------+ |
| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Firewall Rules:
Cloud Firewall:
Ingress (Allow):
+------------------------------------------+
| Rule: allow-https |
| Source: 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Target: Load Balancer |
| Ports: TCP 443 |
+------------------------------------------+
| Rule: allow-sip |
| Source: Carrier IPs (whitelist) |
| Target: Kamailio VMs |
| Ports: UDP/TCP 5060, TCP 5061 |
+------------------------------------------+
| Rule: allow-rtp |
| Source: 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Target: RTPEngine VMs |
| Ports: UDP 10000-60000 |
+------------------------------------------+
Egress (Default Allow):
+------------------------------------------+
| All outbound traffic allowed |
| NAT Gateway for external access |
+------------------------------------------+
Deny (Default):
+------------------------------------------+
| All other ingress denied by default |
+------------------------------------------+
Kubernetes Network Policies:
Pod Network Policy:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: api-manager-policy
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: bin-api-manager
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
ingress:
- from:
- ipBlock:
cidr: 10.0.0.0/16 # Internal VPC only
ports:
- port: 443
- port: 9000
- port: 2112
egress:
- to:
- ipBlock:
cidr: 10.0.0.0/16 # Internal VPC
- to:
- ipBlock:
cidr: 0.0.0.0/0 # External (for webhooks)
ports:
- port: 443
Input Validation
All inputs validated at API boundary:
Validation Layers:
Input Validation Stack:
1. OpenAPI Schema Validation:
+------------------------------------------+
| - Required fields present |
| - Field types correct (string, int, etc)|
| - Enum values valid |
| - String length limits |
+------------------------------------------+
2. Business Logic Validation:
+------------------------------------------+
| - Phone number format (+E.164) |
| - UUID format |
| - Resource exists |
| - Sufficient balance |
+------------------------------------------+
3. SQL Injection Prevention:
+------------------------------------------+
| - Parameterized queries only |
| - No string concatenation for SQL |
| - ORM with escaping (Squirrel) |
+------------------------------------------+
Parameterized Query Example:
Safe Query Pattern:
// CORRECT - Parameterized
query := sq.Select("*").
From("calls").
Where(sq.Eq{"customer_id": customerID}).
Where(sq.Eq{"id": callID})
// Generated SQL:
// SELECT * FROM calls
// WHERE customer_id = ? AND id = ?
// Parameters: [customerID, callID]
// WRONG - String concatenation (NEVER DO THIS)
// query := "SELECT * FROM calls WHERE id = '" + callID + "'"
Rate Limiting
Protect against abuse:
Rate Limit Configuration:
Rate Limiting Strategy:
Global Limits (per customer):
+------------------------------------------+
| Endpoint | Limit |
+------------------------------------------+
| API requests | 1000/minute |
| Call creation | 100/minute |
| SMS sending | 100/minute |
| Login attempts | 10/minute |
+------------------------------------------+
Burst Handling:
+------------------------------------------+
| Token bucket algorithm |
| Bucket size: 2x rate limit |
| Refill rate: Rate limit per second |
+------------------------------------------+
Response on Limit:
+------------------------------------------+
| Status: 429 Too Many Requests |
| Header: Retry-After: 60 |
| Body: {"error": "rate_limit_exceeded"} |
+------------------------------------------+
DDoS Protection:
Cloud Armor Configuration:
WAF Rules:
+------------------------------------------+
| Rule: block-known-attackers |
| - Block IPs from threat intelligence |
+------------------------------------------+
| Rule: rate-limit-by-ip |
| - 10,000 requests/minute per IP |
+------------------------------------------+
| Rule: geo-restrict (optional) |
| - Allow specific countries only |
+------------------------------------------+
Adaptive Protection:
+------------------------------------------+
| - ML-based attack detection |
| - Automatic rule suggestions |
| - Alert on anomalies |
+------------------------------------------+
Audit Logging
Complete audit trail:
Logged Events:
Audit Log Events:
Authentication:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Login success/failure |
| o Logout |
| o Token refresh |
| o Access key creation/revocation |
+------------------------------------------+
Resource Operations:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Create (who, what, when) |
| o Update (who, what, old, new, when) |
| o Delete (who, what, when) |
+------------------------------------------+
Security Events:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Permission denied attempts |
| o Rate limit exceeded |
| o Invalid token attempts |
| o Suspicious activity patterns |
+------------------------------------------+
Log Format:
Audit Log Entry:
{
"timestamp": "2026-01-20T12:00:00.000Z",
"event_type": "resource_created",
"customer_id": "uuid",
"agent_id": "uuid",
"resource_type": "call",
"resource_id": "uuid",
"action": "create",
"source_ip": "192.168.1.100",
"user_agent": "VoIPBIN-SDK/1.0",
"request_id": "uuid",
"details": {
"source": "+15551234567",
"destination": "+15559876543"
}
}
Data Protection
Protecting sensitive data:
Data Classification:
Data Sensitivity Levels:
Public:
+------------------------------------------+
| o API documentation |
| o Service status |
+------------------------------------------+
Internal:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Call metadata (IDs, timestamps) |
| o Flow definitions |
| o Configuration |
+------------------------------------------+
Confidential:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Customer PII (names, emails) |
| o Phone numbers |
| o Call recordings |
| o Chat transcripts |
+------------------------------------------+
Restricted:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Passwords (hashed, never stored plain) |
| o API keys |
| o JWT signing keys |
| o Database credentials |
+------------------------------------------+
Encryption at Rest:
Data Encryption:
Cloud SQL:
+------------------------------------------+
| Encryption: AES-256 |
| Key Management: Google-managed |
| Automatic encryption of all data |
+------------------------------------------+
Cloud Storage (Recordings):
+------------------------------------------+
| Encryption: AES-256 |
| Key Management: Customer-managed (CMEK) |
| Per-object encryption |
+------------------------------------------+
Redis (Memorystore):
+------------------------------------------+
| Encryption: AES-256 |
| In-transit encryption enabled |
+------------------------------------------+
Data Retention:
Retention Policies:
+------------------------------------------+
| Data Type | Retention | Deletion |
+------------------------------------------+
| Call records | 2 years | Soft |
| Call recordings | 90 days | Hard |
| Chat messages | 1 year | Soft |
| Audit logs | 7 years | Hard |
| Session tokens | 1 hour | Automatic |
+------------------------------------------+
Soft Delete:
+------------------------------------------+
| tm_delete set to deletion time |
| Data remains in DB but not returned |
| Can be restored if needed |
+------------------------------------------+
Compliance
Security standards adherence:
Security Standards:
Compliance Framework:
SOC 2 Type II:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Security controls documented |
| o Annual audit |
| o Continuous monitoring |
+------------------------------------------+
GDPR:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Data subject rights supported |
| o Data portability APIs |
| o Right to deletion implemented |
| o EU data residency option |
+------------------------------------------+
HIPAA (Optional):
+------------------------------------------+
| o BAA available for healthcare customers |
| o PHI handling procedures |
| o Audit controls |
+------------------------------------------+
PCI DSS:
+------------------------------------------+
| o No credit card data stored |
| o Payment via Stripe (PCI compliant) |
+------------------------------------------+
Security Best Practices
Development and operations security:
Development:
Secure Development:
Code Review:
+------------------------------------------+
| o All changes peer-reviewed |
| o Security checklist for PRs |
| o Automated security scanning (SAST) |
+------------------------------------------+
Dependency Management:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Regular dependency updates |
| o Vulnerability scanning (Snyk/Dependabot)|
| o No known vulnerable dependencies |
+------------------------------------------+
Secret Handling:
+------------------------------------------+
| o No secrets in code or git |
| o Environment variables for config |
| o Secret rotation procedures |
+------------------------------------------+
Operations:
Security Operations:
Access Control:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Least privilege principle |
| o MFA for all admin access |
| o Regular access reviews |
+------------------------------------------+
Incident Response:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Documented incident procedures |
| o On-call rotation |
| o Post-incident reviews |
+------------------------------------------+
Monitoring:
+------------------------------------------+
| o Real-time security alerts |
| o Failed login monitoring |
| o Anomaly detection |
+------------------------------------------+